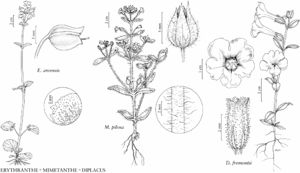
Diplacus fremontii
Phytoneuron 2012-39: 28. 2012.
Herbs, annual. Stems erect, 10–200 (–240) mm, glandular-puberulent or glandular-pubescent. Leaves basal and cauline, basal in rosette, cauline reduced distally; petiole absent; blade narrowly elliptic, sometimes obovate to oblanceolate, 2–30 (–55) × 1–10 (–16) mm, margins entire, sometimes crenate to serrate, plane, apex rounded to acute, surfaces: proximals glabrous, distals glandular-puberulent or glandular-pubescent. Pedicels 1–4 (–7 on proximal) mm in fruit. Flowers 1 per node, chasmogamous. Calyces symmetrically attached to pedicels, inflated in fruit, 5–14 mm, glandular-puberulent to glandular-pubescent or ribs almost tomentose and viscid, lobes subequal, apex rounded and apiculate or acute, intercostal areas white. Corollas magenta to dark reddish purple, throat often darker near mouth, palate ridges yellow at mouth, throat floor glabrous or minutely puberulent, tube-throat 9–23 mm, limb 8–26 mm diam., not bilabiate. Anthers included, glabrous, rarely minutely puberulent. Styles minutely puberulent. Stigmas included, lobes subequal. Capsules 6.5–13 (–14) mm. 2n = 16.
Phenology: Flowering Mar–Jun.
Habitat: Soft, sandy soils along washes, flood plains, areas of water runoff, sandy hilltops and flats.
Elevation: 100–2100 m.
Distribution
Calif., Mexico (Baja California)
Discussion
Diplacus fremontii occurs from Monterey and San Benito counties south to San Diego County, east to Kern County and adjacent Inyo County, and in Baja California.
Selected References
None.