Boschniakia
Mém. Acad. Imp. Sci. Saint-Pétersbourg, Sér. 6, Sci. Math. 2: 159. 1832.
| Taxon | Illustrator ⠉ | |
|---|---|---|
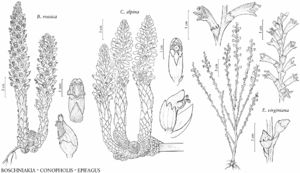 | Boschniakia rossica Conopholis alpina Epifagus virginiana | John Myers John Myers John Myers |
Herbs, monocarpic perennial; achlorophyllous, holoparasitic, with rhizomelike vegetative structure, surfaces tessellate or with irregular scaly plates, roots absent. Stems erect, fleshy, glabrous. Leaves cauline, spiral, proximally imbricate, less so distally; petiole absent; blade stiffly chartaceous, margins entire. Inflorescences terminal, dense spikes; bracts present. Pedicels absent; bracteoles absent. Flowers: sepals 4 or 5, calyx bilaterally symmetric, cupshaped, lobes triangular-acuminate; petals 5, corolla dark red or dark purple, strongly bilabiate, cucullate, short-tubular, palatal folds absent, abaxial lobes 0 or 3, adaxial 2, adaxial lip entire or with shallow notch; stamens 4, didynamous, included, filaments glabrous; staminode 0; ovary 1-locular, placentation parietal; stigma 2–4-lobed, broadly clavate-crateriform or nearly capitate. Capsules: dehiscence loculicidal. Seeds 2000–2500, light tan or brown, irregularly columnar or oblong-ellipsoid, wings absent.
Distribution
nw North America, Asia (Bhutan), Asia (China), Asia (Nepal), Asia (Russian Far East)
Discussion
Species 2 (1 in the flora).
Boschniakia has not been well studied using modern systematic techniques. The overall relationship of the genera of holoparasites in Orobanchaceae is currently under review.
Boschniakia himalaica Hooker f. & Thomson is distributed in southern China and the Himalayan countries of Asia. It is parasitic on species of Rhododendron.