Centaurea solstitialis
Sp. Pl. 2: 917. 1753.
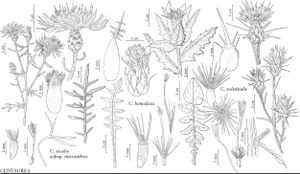
Annuals, 10–100 cm. Stems simple or often branched from base, forming rounded bushy plants, gray-tomentose. Leaves gray-tomentose and scabrous to short-bristly; basal and proximal cauline petiolate or tapered to base, usually absent at anthesis, blades 5–15 cm, margins pinnately lobed or dissected; cauline long-decurrent, blades linear to oblong, 1–10 cm, entire. Heads disciform, borne singly or in open leafy arrays, long-pedunculate. Involucres ovoid, 13–17 mm, loosely cobwebby-tomentose or becoming glabrous. Principal phyllaries: bodies pale green, ovate, appendages stramineous to brown, each with palmately radiating cluster of spines, and stout central spine 10–25 mm. Inner phyllaries: appendages scarious, obtuse or abruptly spine-tipped. Florets many; corollas yellow, all ± equal, 13–20 mm; sterile florets slender, inconspicuous. Cypselae dimorphic, 2–3 mm, glabrous, outer dark-brown, without pappi, inner white or light-brown, mottled; pappi of many white, unequal bristles 2–4 mm, fine. 2n = 16.
Phenology: Flowering mostly summer–autumn (Jun–Oct), sometimes year-round in frostfree coastal habitats.
Habitat: Roadsides, fields, pastures, woodlands
Elevation: 0–2000 m
Distribution
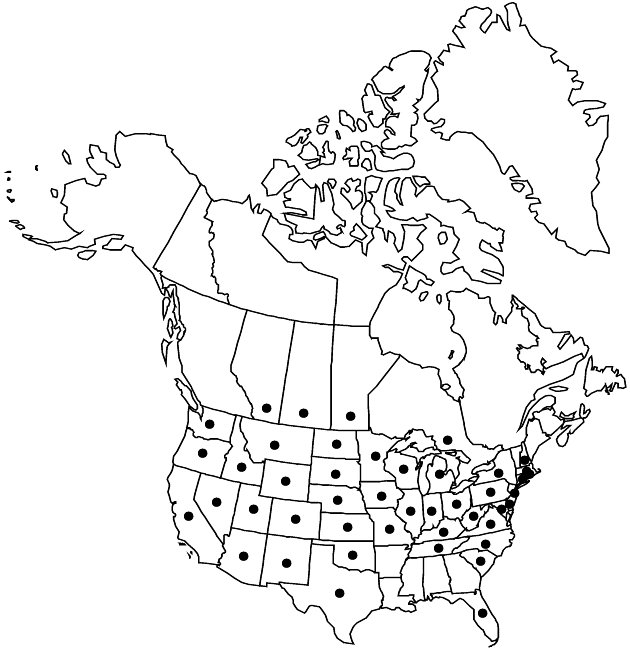
Introduced; Widely, Alta., Man., Ont., Sask., Ariz., Calif., Colo., Conn., Del., Fla., Idaho, Ill., Ind., Iowa, Kans., Ky., Md., Mass., Mich., Minn., Mo., Mont., Nebr., Nev., N.H., N.J., N.Mex., N.Y., N.C., N.Dak., Ohio, Okla., Oreg., Pa., R.I., S.C., S.Dak., Tenn., Tex., Utah, Va., Wash., W.Va., Wis., Wyo., s Europe
Discussion
Centaurea solstitialis is a serious weed pest, especially in the western United States, where it has invaded millions of acres of rangelands, and it is listed as a noxious weed in eleven western states and two Canadian provinces. It is a strong competitor in infested areas, often forming dense colonies. It is very difficult to control or eradicate once it becomes established. In addition, yellow star-thistle is poisonous to horses; when ingested over a prolonged period it causes a neurological disorder called equine nigropallidal encephalomalacia, or “chewing disease.” Although its bitter taste and spiny heads usually deter grazing animals, horses sometimes will seek it out. Yellow star-thistle tends to spread in rangelands when more palatable plants are consumed.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
"fine" is not a number."fine" is not a number.