Artemisia papposa
Leafl. W. Bot. 6: 43, plate 1. 1950.
Shrubs, 5–15 (–20) cm (not cespitose), aromatic. Stems relatively numerous, erect, gray, simple (annual flowering branches leafy), loosely sericeous. Leaves (semideciduous) cauline (sessile), gray-green; blades oblanceolate, 0.5–3 × 0.2–1.5 cm (bases attenuate), 3-lobed or irregularly palmatifid (lobes narrow, apices acute), sparsely sericeous-lanate. Heads (mostly erect, peduncles 0 or to 25 mm) in racemiform arrays (4–) 8–12 (–14) × (0.5–) 1–2 (–4) cm. Involucres globose, 3.5–5 × 4–5 mm. Phyllaries ovate, sparsely sericeous. Florets: pistillate 8; bisexual 20–35; corollas yellow (tubular with broad throats), ca. 2 mm, glandular. Cypselae (light-brown) oblanceoloid (4–5-angled, broadest at truncate apices), 0.3–0.5 mm, glandular-pubescent (pappi coroniform, 0.3–0.6 mm, irregularly lacerate).
Phenology: Flowering early spring–mid summer.
Habitat: Rocky swales, dry meadows, alkaline mud flats
Elevation: 1400–2100 m
Distribution
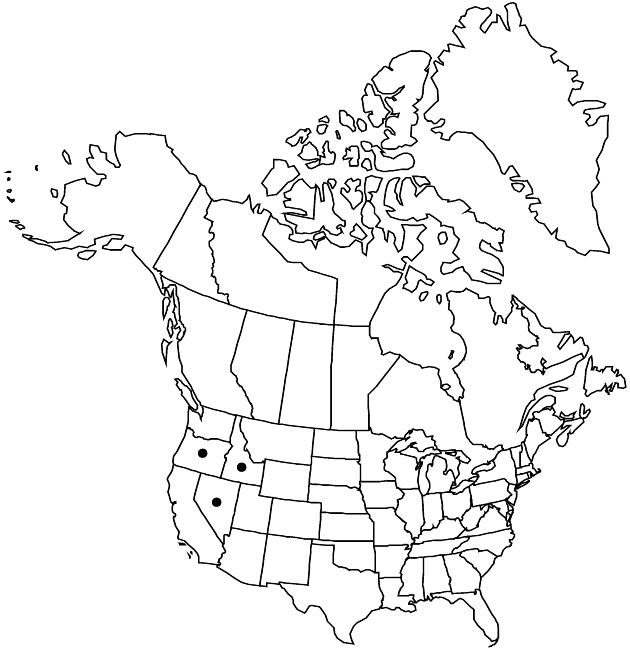
Idaho, Nev., Oreg.
Discussion
The pappose cypselae make Artemisia papposa anomalous within Artemisia. Artemisia papposa has capitulescence characteristics that suggest a relationship to Sphaeromeria.
Selected References
None.