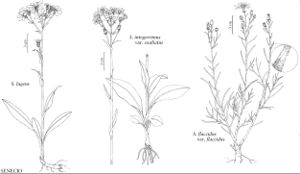
Senecio lugens
in J. Franklin et al., Narr. Journey Polar Sea, 748. 1823.
Perennials, (10–) 20–35 (–50) cm (rhizomes suberect to creeping). Herbage loosely, often unevenly, floccose-tomentose, glabrescent. Stems single or clustered. Leaves reduced distally; petiolate; blades narrowly obovate to oblanceolate, (4–) 8–18 (–25) cm, bases tapered, margins subentire to dentate (denticles callous; mid and distal leaves bractlike, clasping). Heads (2–) 7–12 (–20+) in corymbiform arrays. Calyculi of 2–5 linear bractlets (1–2 mm). Phyllaries (± 8) ± 13 (± 21), 4–7 mm, tips black. Ray-florets (± 5) ± 8 (± 13); corolla laminae 8–10 (–15) mm. Cypselae glabrous. 2n = 40, 80.
Phenology: Flowering summer.
Habitat: Moist meadows, gravelly streambeds, open woods in alpine or boreal sites
Elevation: 200–2500 m
Distribution
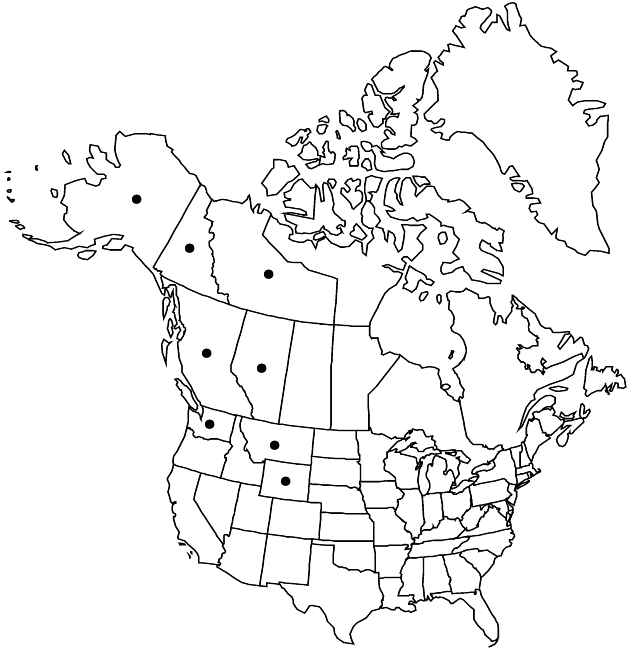
Alta., B.C., N.W.T., Yukon, Alaska, Mont., Wash., Wyo.
Discussion
Senecio lugens varies greatly in robustness across its range. It is scattered widely in the Rocky Mountain uplift and adjacent regions from northern Wyoming to Alaska; it is disjunct in the Olympic Peninsula, Washington. Superficially similar to S. integerrimus, S. lugens has well-developed, coarse, spreading rootstocks with branching roots; S. integerrimus arises from foreshortened, buttonlike caudices with abundant unbranched, fleshy-fibrous roots.
Selected References
None.