Packera quercetorum
Kew Bull. 47: 101. 1992.
Perennials, 60–100+ cm; taprooted (caudices subligneous, ascending to erect). Stems 1 or 2–4, clustered (proximally deeply purple-tinged, distally lightly tinged), glabrous or tomentose at bases and in leaf-axils. Basal leaves (and proximal cauline) petiolate; blades obovate or lyrate (pinnately lobed, lateral lobes 2–6+ pairs, their bases petioluliform, terminal lobes larger than laterals, midribs narrowly winged), 60–160+ × 20–40+ mm, bases wide, ultimate margins sharply dentate, crenate-dentate, or irregularly incised. Cauline leaves gradually reduced (petiolate or sessile; shallowly lobed, midribs ± winged, distals bractlike, dentate to incised). Heads 15–40+ in open, cymiform arrays. Peduncles ebracteate, glabrous. Calyculi inconspicuous. Phyllaries (13–) 21, green (tips yellow), 5–7 mm, glabrous (tips sometimes hairy). Ray-florets (8–) 13; corolla laminae 6–10+ mm. Disc-florets 60–70+; corolla-tubes 2–3 mm, limbs 3.5–4.5 mm. Cypselae 1.5–2 mm, glabrous or ± scabrellous; pappi 5.5–6.5 mm. 2n = 92.
Phenology: Flowering mid Apr–early Jun.
Habitat: Rocky soils, open areas, scrub-oak and pinyon-pine forests, chaparral
Elevation: 800–2200 m
Discussion
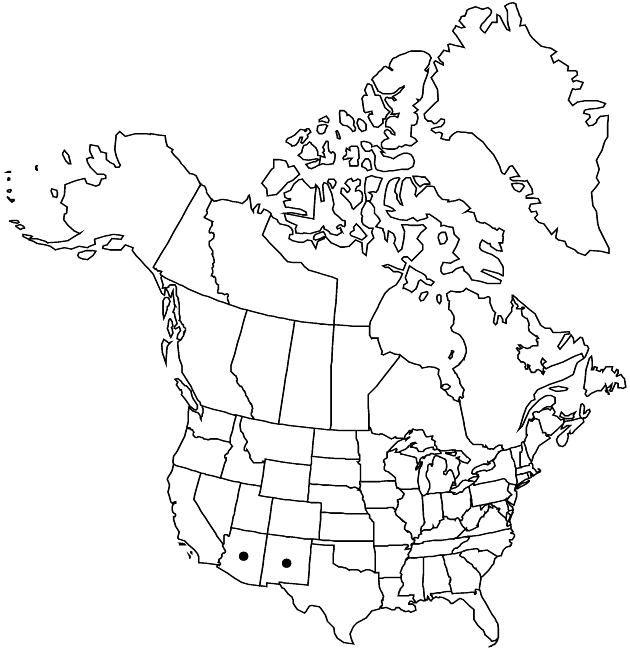
Packera quercetorum is found only infrequently and in relatively small populations in central and southern Arizona and west-central New Mexico. The plants are robust and have probable affinities to P. multilobata. The plants have a bluish tinge when freshly collected and are distinctive in the field.
Selected References
None.