Amphipappus
Boston J. Nat. Hist. 5: 107. 1845.
| Taxon | Illustrator ⠉ | |
|---|---|---|
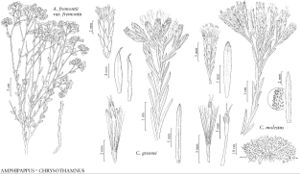 | Amphipappus fremontii Chrysothamnus greenei Chrysothamnus molestus | Barbara Alongi John Myers John Myers |
Shrubs, 30–60 cm (rounded). Stems erect (bark whitish), intricately branched, becoming leafless and spinescent, branchlets glabrous or densely, hirtellous. Leaves cauline; alternate (ascending); petiolate to subsessile; blades 1-nerved, obovate to narrowly elliptic, margins entire, faces glabrous or hirtellous, often resinous. Heads radiate (discoid), (2–4) in glomerate, terminal clusters, these in corymbiform arrays. Involucres turbino-cylindric, 4–5.5 × 2–3 mm. Phyllaries 7–12 in 3 series, greenish white, 1-nerved (outer keeled), ovate to elliptic, unequal, thin-indurate, margins not scarious, faces glabrous. Receptacles flat, pitted, epaleate. Ray-florets (0–) 1–2, pistillate, fertile; corollas yellow (laminae slightly longer than involucres). Disc-florets 3–7, functionally staminate; corollas yellow, tubes longer than narrowly funnelform throats (nerves 1, yellow, not resinous), lobes 5, reflexed or coiling back, lanceolate; style-branch appendages triangular (nonfunctional, lacking stigmatic lines). Cypselae (ray) oblongelliptic to obovoid, ± flattened, 2-nerved, faces moderately villous; pappi persistent, of 15–20, stramineous, basally connate, flattened, slender, barbellate, apically attenuate bristles in 1 series (disc bristles longer than ray, sometimes undulate or twisted). x = 9.
Distribution
sw United States
Discussion
Species 1.
Amphipappus is characterized by its low-shrubby, intricately branched habit and corymbiform, glomerate clusters of small, few-flowered heads, functionally staminate disc florets, and pappi of short, barbellate bristles, the fertile ray cypselae with pappi of shorter, flattened bristles. The genus is restricted to the Mojave Desert of California, Nevada, Utah, and Arizona where these states are contiguous.