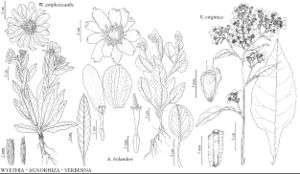
Wyethia
J. Acad. Nat. Sci. Philadelphia 7: 39, plate 5. 1834.
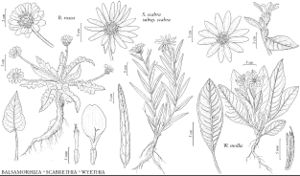
Perennials, 15–60 (–100) cm (taproots relatively massive; caudices seldom branched). Stems erect (or bending erect from bases), branched mostly from bases. Leaves basal and cauline; alternate; usually petiolate (basal), sometimes sessile; blades (usually pinnately nerved, basal larger than cauline) ± deltate, elliptic-ovate, lanceolate, lance-elliptic, lance-linear, or oblong-ovate, bases truncate to cuneate, margins usually entire, rarely dentate to serrate (sometimes ciliate), faces glabrous or hairy (sometimes glanddotted or finely stipitate-glandular). Heads radiate, borne singly or 2–5 (–8+) in ± corymbiform to racemiform arrays. Involucres hemispheric to campanulate or turbinate, 12–60+ mm diam. Phyllaries persistent, 12–36 (–48) in 2–3+ series (subequal to unequal, outer sometimes foliaceous, much larger than inner). Receptacles flat to convex, paleate (paleae conduplicate, at least bases, papery). Ray-florets 5–25+, pistillate, fertile; corollas mostly yellow (cream to white in W. helianthoides). Disc-florets 35–150+, bisexual, fertile; corollas yellow, tubes much shorter than cylindric throats; lobes 5, ± deltate to lanceolate (style-branches stigmatic in 2 barely distinct lines, appendages ± filiform). Cypselae ± prismatic, weakly 3–4-angled (faces glabrous or hairy); pappi 0, or persistent, coroniform (usually lacerate) or of 1–4+ ovate to subulate, erose to lacerate (often basally connate) scales. x = 19.
Distribution
w North America
Discussion
Species 8 (8 in the flora).
Some species formerly included in Wyethia are here treated in Agnorhiza and Scabrethia. Balsamorhiza is closely related to Wyethia.
Selected References
Lower Taxa
Key
| 1 | Involucres 35–60+ mm diam.; outer phyllaries (30–)40–80+ mm (± foliaceous, much surpassing discs) | > 2 |
| 1 | Involucres 10–30(–40) mm diam.; outer phyllaries 15–30(–40) mm (not foliaceous, seldom surpassing discs) | > 3 |
| 2 | Leaf blades: faces glabrous or finely stipitate-glandular, sometimes sparsely pilosulous as well (usually shining); cypselae 10–13 mm | Wyethia glabra |
| 2 | Leaf blades: faces densely tomentose to tomentulose (usually gland-dotted as well), glabrescent; cypselae 12–15 mm | Wyethia helenioides |
| 3 | Leaf blades: faces tomentose to tomentulose (at least when young, glabrescent, usuallygland-dotted) | Wyethia mollis |
| 3 | Leaf blades: faces glabrous, glabrate, hirsute, hirsutulous, hirtellous, pilose, pilosulous, scabrellous, or strigillose (not tomentose to tomentulose, often gland-dotted or stipitate-glandular) | > 4 |
| 4 | Leaf blades: faces glabrous or glabrate (gland-dotted); phyllary margins not ciliate; cypselae glabrous | > 5 |
| 4 | Leaf blades: faces usually hirsute, hirsutulous, hirtellous, pilose, pilosulous, scabrellous, or strigillose (sometimes vernicose, rarely finely stipitate-glandular or gland-dotted), sometimes glabrate; phyllary margins ± ciliate; cypselae strigillose or glabrous | > 6 |
| 5 | Basal leaves: blades lance-elliptic or oblong-lanceolate to lanceolate; rays 8–21(–25), laminae 25–60 mm; cypselae 8–9 mm | Wyethia amplexicaulis |
| 5 | Basal leaves: blades narrowly oblong-lanceolate to lance-linear; rays 5–8+, lami-nae 18–30 mm; cypselae 6–8 mm | Wyethia longicaulis |
| 6 | Basal leaves: blades lanceolate to lance-linear; cypselae 7–8 mm, ± strigillose | Wyethia angustifolia |
| 6 | Basal leaves: blades elliptic-ovate, lanceolate, or lance-elliptic; cypselae 9–11 mm, strigillose or glabrous | > 7 |
| 7 | Phyllaries 36–48; rays 13–25, laminae (cream to white) 25–45 mm; cypselae strigillose distally and on margins | Wyethia helianthoides |
| 7 | Phyllaries 16–34; rays 11–12, laminae (yellow) 25–50 mm; cypselaeglabrous | Wyethia arizonica |
"broader" is not a number.