Melanthera
Skr. Naturhist.-Selsk. 2: 213. 1792.
| Taxon | Illustrator ⠉ | |
|---|---|---|
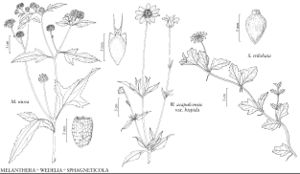 | Melanthera nivea Wedelia acapulcensis var. hispida Sphagneticola trilobata | Yevonn Wilson-Ramsey Yevonn Wilson-Ramsey Bee F. Gunn |
Perennials or subshrubs, 30–220 cm. Stems usually erect or spreading, sometimes sprawling or scandent, branched throughout (± 4-angled and sulcate, usually scabro-hispid, caudices usually ± woody, often ± spheric). Leaves cauline; opposite; petiolate or nearly sessile; blades (usually 3-nerved) usually lance-elliptic, linear, oblanceolate, ovate-elliptic, or ovate, sometimes deltate to 3-lobed, bases cuneate to truncate (sometimes hastate or with antrorse basal lobes), margins crenate or serrate (often irregularly), faces usually scabro-hispid, sometimes glabrescent. Heads discoid [radiate], borne singly or in loose, corymbiform arrays. Involucres ± hemispheric or broader, 6–20 mm diam. Phyllaries persistent, mostly 8–16 in 2–3 series (mostly ovate to lanceolate, subequal to unequal, bases pallid, with or without green veins, apices herbaceous, tips usually ± mucronate). Receptacles flat to convex or convex-hemispheric, paleate (paleae oblanceolate, conduplicate, apices mucronate, pungent, erect or spreading to recurved). Ray-florets 0 [8–15]. Disc-florets 20–100+, bisexual; corollas white [pale to bright-yellow], tubes shorter than narrowly funnelform to cylindric throats, lobes 5, ± deltate (anther sacs black; style-branches stigmatic in 2 lines, appendages lance-triangular, papillate). Cypselae (± brown) obpyramidal, (3–) 4-angled, not or slightly compressed (striate, rarely verrucose-tuberculate, glabrous); pappi readily falling, of 2–12 barbellulate bristles or awns. x = 15.
Distribution
North America, Mexico, West Indies, Central America, South America, Africa
Discussion
Species ca. 20 (3 in the flora).
Melanthera is common as a strand and weedy plant in Mexico, the West Indies, Central America, South America, and sub-Saharan Africa. In the flora, Melanthera is distinguished by its lack of ray florets, white disc corollas, distinctive cypselae, and delicate, caducous pappus awns. Tilesia G. F. W. Meyer (= Wulffia Necker ex Cassini), Wollastonia de Candolle ex Decaisne, and Echinocephalum Gardner are closely related to Melanthera. The type of Echinocephalum (South America; rays neuter, corollas pale yellow) may be congeneric with that of Melanthera. Inclusion of African species (all radiate) in Melanthera further broadens and complicates its delimitation. H. Wild (1965) broadened the circumscription even more by including the unispecific Wollastonia among African Melanthera species with styliferous ray florets.
Selected References
Lower Taxa
Key
| 1 | Leaf blades usually linear to narrowly lanceolate-oblanceolate, rarely narrowly ovate-elliptic; peduncles glabrescent; phyllaries ovate, 4–5 × 2–3 mm; mucros on paleae 0.5–1 mm, straight to slightly recurved | Melanthera angustifolia |
| 1 | Leaf blades usually ovate, sometimes deltate or 3-lobed, rarely lanceolate-elliptic; peduncles hispid to strigose; phyllaries broadly ovate to lanceolate, 5–7 × 1.5–3 mm, or 3–10 × 3–4 mm; mucros on paleae 0.5–1.5 mm, usually notably recurved | > 2 |
| 2 | Plants 30–60 cm; stems sprawling to weakly erect; leaf blades 1.5–4 × 1–1.5 cm; florets 25–40 | Melanthera parvifolia |
| 2 | Plants 50–220 cm; stems usually erect, sometimes sprawling or scandent; leaf blades 5–12 × 3–8 cm; florets 30–100+ | Melanthera nivea |
"broader" is not a number.