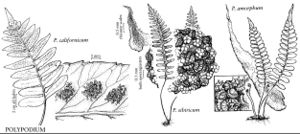
Polypodium californicum
Enum. Filic. 102. 1824.
Stems dull or inconspicuously glaucous, moderately stout, to 10 mm diam., acrid or bland-tasting; scales uniformly brown or slightly darker near point of attachment, lanceolate-ovate, symmetric, margins entire to erose. Leaves to 70 cm. Petiole usually slender, to 3 mm diam. Blade deltate to lanceolate-ovate, pinnatifid, usually widest near base, to 20 cm wide, leathery to herbaceous; rachis sparsely scaly to glabrescent abaxially, puberulent adaxially; scales deltate to ovate, usually more than 10 cells wide. Segments linear-lanceolate to oblong, usually less than 15 mm wide; margins serrate; apex widely obtuse to rarely attenuate; midrib puberulent adaxially. Venation weakly to conspicuously anastomosing, most segments containing several areoles, often forming 1 row. Sori midway between margin and midrib or slightly closer to midrib, usually less than 3 mm diam., oval when immature. Sporangiasters absent. Spores less than 58 µm, verrucose, with surface projections to 3 µm. 2n = 74.
Phenology: Sporulating early winter–spring.
Habitat: Cliffs and soil on rocky slopes, on a variety of substrates but usually igneous
Elevation: 0–1500 m.
Distribution
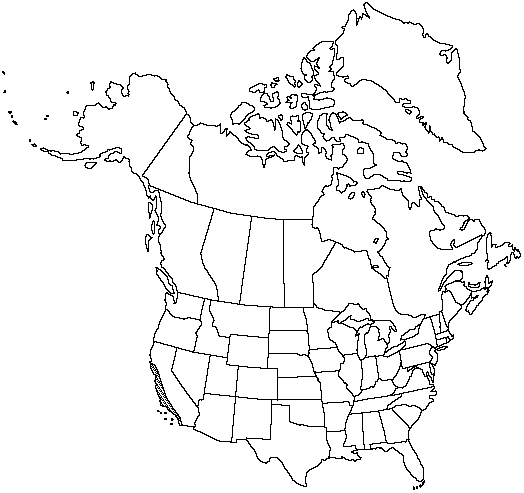
Calif., Mexico in Baja California
Discussion
R. M. Lloyd and F. A. Lang (1964) recognized two cytotypes within Polypodium californicum. The tetraploid has proved to be an allopolyploid involving P. californicum and P. glycyrrhiza and is treated here as a separate species, P. calirhiza, following S. A. Whitmore and A. R. Smith (1991). Polypodium californicum can be confused with P. calirhiza, but it usually can be distinguished by blade shape, venation, spore size, and geographic distribution. D. S. Barrington et al. (1986) reported that spores of northern populations of P. californicum can be as large as those of P. calirhiza, but the former species has veins forming more areoles per segment than does the latter.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
"widest" is not a number.