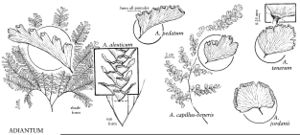
Adiantum jordanii
Bot. Zeitung 1864: 26. 1864.
Stems short-creeping; scales reddish-brown, concolored, margins entire. Leaves arching or pendent, clustered, 30–45 cm. Petiole 1–1.5 mm diam., glabrous, not glaucous. Blade lanceolate, pinnate, 20–24 × 8–10 cm, gradually reduced distally, glabrous; proximal pinnae 3 (–4) -pinnate; rachis straight, glabrous, not glaucous. Segment stalks 1–4 mm, with dark color ending abruptly at segment base. Ultimate segments fan-shaped, not quite as long as broad; base truncate or broadly cuneate; margins of fertile segments unlobed but very narrowly incised, sterile segments with margins lobed, denticulate; apex rounded. Indusia transversely oblong, 3–10 mm, glabrous. Spores mostly 40–50 µm diam. 2n = 60.
Phenology: Sporulating early spring–midsummer.
Habitat: Seasonally moist, shaded, rocky banks, canyons, and ravines
Elevation: 0–1000 m
Distribution
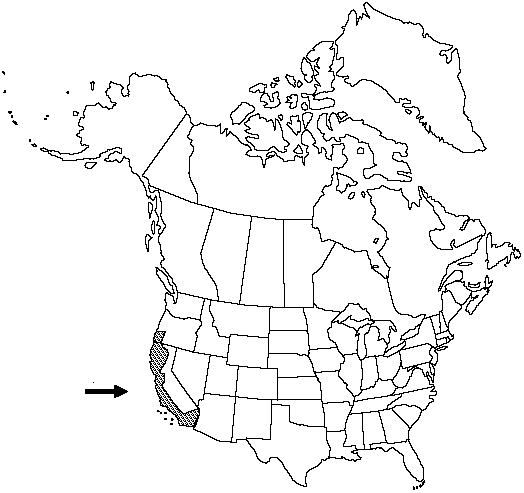
Calif., Oreg., Mexico in Baja California
Discussion
Adiantum jordanii occasionally hybridizes with A. aleuticum where their ranges overlap in northern California, yielding the sterile hybrid Adiantum × tracyi C. C. Hall ex W. H. Wagner. Adiantum × tracyi, morphologically intermediate between its parental species, can be distinguished from A. jordanii by its broadly deltate leaf blade that tapers abruptly from the 4(–5)-pinnate base to a 1-pinnate apex. It is best separated from A. aleuticum by leaf blades with a strong rachis, and by ultimate blade segments that are less than twice as long as broad. Adiantum × tracyi shows 59 univalents at metaphase; its spores are irregular and misshapen (W. H. Wagner Jr. 1962).
Selected References
None.