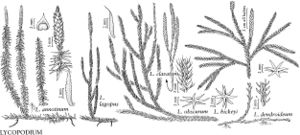
Lycopodium hickeyi
Beitel, & R. C. Moran, Amer. Fern J. 79: 119–121. 1989.
Horizontal stems subterranean. Upright shoots treelike, many branched, branchlets numerous and strongly differentiated; annual bud constrictions absent; leaves on main axis below lateral branchlets tightly appressed, dark green, needlelike, 3.5–4.5 × 0.5–0.6 mm, soft. Lateral branchlets round in cross-section, 4–7 mm diam.; annual bud constrictions inconspicuous; leaves ascending, in 6 ranks, 1 on upperside, 4 lateral, and 1 on underside, equal in size, linear, widest in middle; margins entire; apex acuminate, lacking hair tip. Strobili sessile, 1–7 per upright shoot, 15–65 mm. Sporophylls 3–3.5 × 2–2.5 mm, apex long, gradually narrowing to tip. 2n = 68.
Habitat: Mainly in hardwood forests and second-growth, shrubby habitats
Elevation: 0–1600 m
Distribution
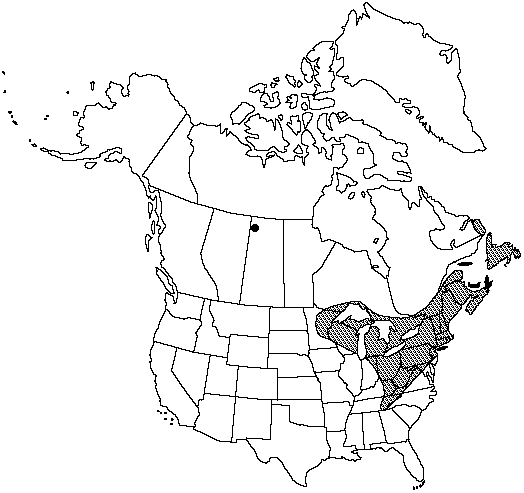
N.B., Nfld. and Labr. (Nfld.), N.S., Ont., P.E.I., Que., Sask., Conn., Ind., Ky., Maine, Md., Mass., Mich., Minn., N.H., N.J., N.Y., N.C., Ohio, Pa., R.I., Tenn., Vt., Va., W.Va., Wis.
Discussion
The range of Lycopodium hickeyi overlaps with that of L. obscurum and extends considerably north and west of that species. Although the arrangement of the leaf ranks is similar to that of L. obscurum, the leaf dimorphy and the ascending orientation and absence of twisting of the leaves are diagnostic. Where ranges of two or three species overlap, indivual species retain their identities, indicating that their critical differences have a genetic basis.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
No values specified.