Juncus castaneus
Fl. Brit. 1: 383. 1800.
Herbs, perennial, strongly rhizomatous, 1–4 dm. Culms solitary, 1–2 mm diam. Cataphylls 1–2. Leaves partially cauline, 3–5, auricles absent distally, rounded proximally; blade channeled, to 20 cm, reduced distally. Inflorescences glomerules, 1–3 (–5), each with 2–10 flowers; peduncles 0.4–1.5 cm; primary bracts somewhat inflated, usually surpassing inflorescence. Flowers: bracteoles absent; tepals brown or occasionally paler, lanceolate, 4.5–6.6 mm, apex acute to obtuse; inner series slightly shorter; stamens 6, filaments 2.5–3.5 mm, anthers 0.6–1.3 mm; style 1–1.3 mm. Capsules chestnut-brown, 3-locular, narrowly oblong, 6.5–8.5 × 1.8–2.3 mm. Seeds pale-yellow, fusiform, body 0.6–0.7 mm, tails 0.8–1.1 mm. 2n = 60, 90, 120.
Phenology: Flowering and fruiting late spring–summer.
Habitat: Tundra, subalpine and alpine bogs and meadows, and along streams in gravelly or clayey soils
Elevation: 10–3700 m
Distribution
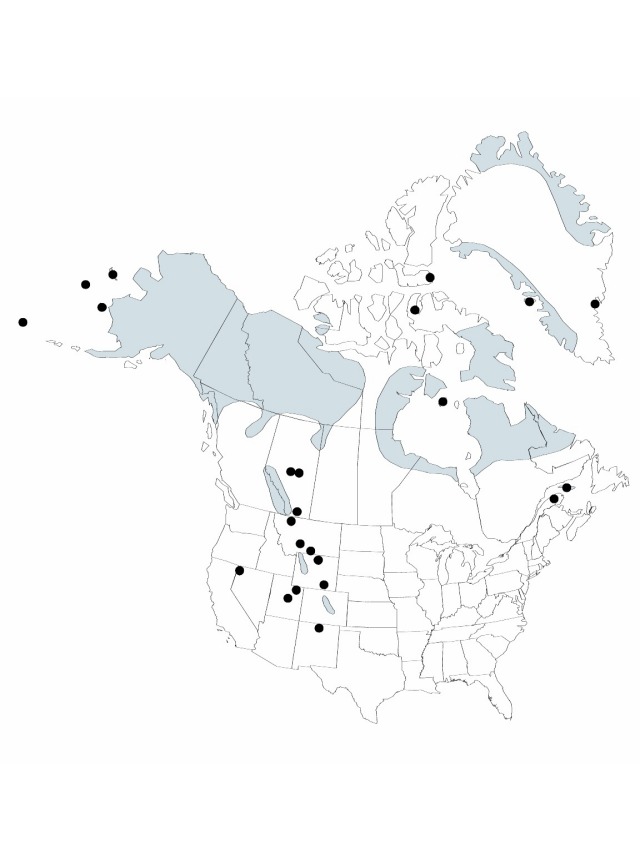
Greenland, Alta., B.C., Man., Nfld. and Labr. (Labr.), N.W.T., Nunavut, Ont., Que., Sask., Yukon, Alaska, Colo., Mont., Nev., N.Mex., Utah, Wyo., Europe, Asia
Discussion
In southern Alaska some plants with several many-flowered heads and capsules about double the length of the perianth have been referred to the Asian Juncus castaneus subsp. leucochlamys. The distinction, however, seems dubious without further investigation.
Selected References
None.
