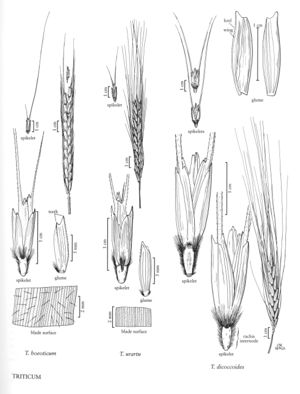
Triticum dicoccoides
Culms to 100 cm, decumbent; nodes glabrous or puberulent; internodes mostly hollow, solid for 1 cm below the spikes. Blades 4-6 mm wide, pubescent. Spikes to 10 cm, wider than thick; rachises densely hairy at the nodes and margins; internodes 3-8 mm; disarticulation spontaneous, dispersal units wedge-shaped. Spikelets 15-25 mm, oblong to rectangular, with 3 florets, usually the lower 2 seed-forming. Glumes 10-15 mm, coriaceous, tightly appressed to the lower florets, 2-keeled, prominent keel winged to the base, 2-toothed, second tooth poorly developed; lemmas 10-15 mm, awned, awns on the lower 2 lemmas to 15 cm, on the third lemma to 2 cm; paleas not splitting at maturity. Endosperm flinty. Haplomes AuB. 2n = 28.
Discussion
Triticum dicoccoides is the wild counterpart of T. dicoccum, and is an ancestor of both T. durum and T. aestivum. Morphologically, it is almost indistinguishable from T. araraticum Jakubz., a wild tetraploid that differs from T. dicoccoides in combining the Ab and G haplomes. Triticum dicoccoides is native to the Fertile Crescent. Its distribution overlaps that of T. araraticum in the northern and eastern portions of the region.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
"decumbent" is not a number."-3timesthelengthof" is not declared as a valid unit of measurement for this property.