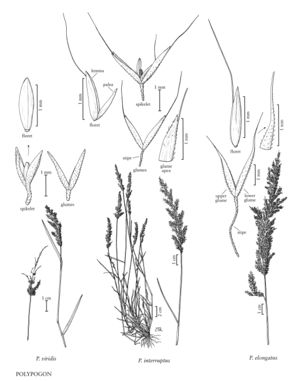
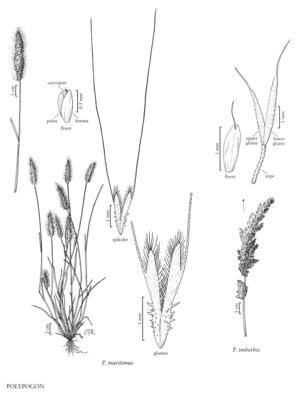
Plants annual or perennial; not rhizomatous. Culms 4-120 cm, erect to decumbent, rooting at the lower nodes, sparingly branched near the base. Leaves usually no more than 5 per culm, basal and cauline; sheaths open, smooth or scabridulous; auricles absent; ligules membranous or hyaline, acute to broadly rounded, erose, ciliate; blades flat to convolute. Inflorescences terminal panicles, dense, continuous or interrupted below; branches flexible, usually some longer than 1 cm; pedicels absent and the spikelets borne on a stipe, or present and terminating in a stipe; stipes scabrous, flaring distally; disarticulation at the base of the stipes. Spikelets 1-5 mm, weakly laterally compressed, with 1 bisexual floret; rachillas not prolonged beyond the base of the floret. Glumes exceeding the floret, lanceolate, bases not fused, apices entire to emarginate or bilobed, usually awned from the sinuses or apices, awns flexuous, glabrous, sometimes unawned; lemmas 1-3 (5) -veined, often awned, awns usually terminal or subterminal, sometimes arising from just above midlength; paleas from 1/3 as long as to equaling the lemmas; lodicules 2, oblong-lanceolate to lanceolate; anthers 3; ovaries glabrous; styles separate. Caryopses slightly flattened, broadly ellipsoid to oblong-ellipsoid; hila 1/6 – 1/4 as long as the caryopses, ovate, x = 7.
Distribution
Idaho, Mont., Wash., Va., Alta., B.C., Man., Ont., Que., Sask., Yukon, Del., Wis., Conn., Mass., Maine, N.H., Pacific Islands (Hawaii), Fla., Wyo., N.J., N.Mex., Tex., La., Nebr., Tenn., N.C., S.C., Pa., N.Y., Calif., Nev., Puerto Rico, Colo., Alaska, Ala., Kans., N.Dak., Okla., S.Dak., Ark., Ga., Ariz., Md., Utah, Minn., Mich., Miss., Oreg.
Discussion
Polypogon is a pantropical and warm-temperate genus of about 18 species. There are eight species in the Flora region; one species, P. interruptus, is native.
Polypogon is similar to Agrostis, and occasionally hybridizes with it. It differs from Agrostis in having spikelets that disarticulate below the glumes, often at the base of a stipe.
Lower Taxa
Key
| 1 | Glumes with awns 3-12 mm long. | > 2 |
| 2 | Glumes deeply lobed, the lobes more than 1/6 the length of the glume body | Polypogon maritimus |
| 2 | Glumes not lobed or the lobes 1/10 or less the length of the glume body. | > 3 |
| 3 | Plants annual; glume apices rounded, lobed, the lobes 0.1-0.2 mm long; ligules 2.5-16 mm long | Polypogon monspeliensis |
| 3 | Plants perennial; glume apices acute to truncate, unlobed or the lobes shorter than 0.1 mm; ligules 1-6 mm long. | > 4 |
| 4 | Glume awns (3)4-6 mm long; longest blades 13-17 cm long | Polypogon australis |
| 4 | Glume awns 1.5-3.2 mm long; longest blades 5-9 cm long | Polypogon interruptus |
| 1 | Glumes unawned or with awns to 3.2 mm long. | > 2 |
| 5 | Glumes unawned | Polypogon viridis |
| 5 | Glumes awned, the awns 0.2-3.2 mm long. | > 6 |
| 6 | Stipes 1.5-2.5 mm long; glumes tapering from about midlength to the acute, unlobed apices | Polypogon elongatus |
| 6 | Stipes 0.2-1.5 mm long; glumes not tapering to the apices, the apices usually rounded to truncate, sometimes acute, often lobed. | > 7 |
| 7 | Lemmas 1-2 mm long; paleas about 1/2 as long as the lemmas; the lower glumes longer than the upper glumes | Polypogon imberbis |
| 7 | Lemmas 0.7-1.5 mm long; paleas from 3/4 as long as to equaling the lemmas; glumes of each spikelet subequal to equal. | > 8 |
| 8 | Plants annual; glumes acute to rounded, lobed, the lobes 0.1-0.2 mm long | Polypogon fugax |
| 8 | Plants perennial, often flowering the first year; glumes acute to truncate, if lobed, the lobes to 0.1 mm long | Polypogon interruptus |
"decumbent" is not a number.