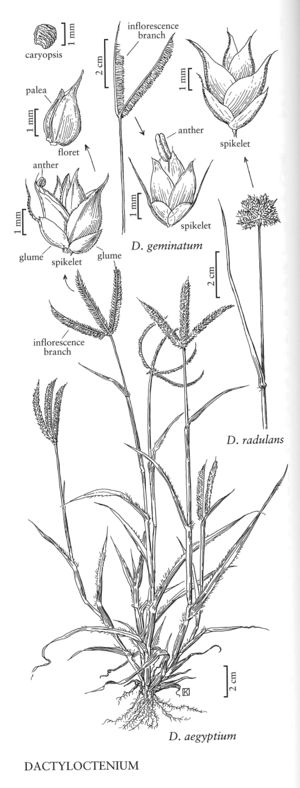
Dactyloctenium radulans
Plants annuals or short-lived perennials. Culms 5-20 (50) cm, decumbent or ascending, rarely erect, usually branched. Sheaths glabrous or with papillose-based hairs, slightly keeled; ligules to 1 mm, membranous, truncate, ciliate; blades flat, bases with papillose-based hairs. Panicle branches 2-11, 0.4-1.5 cm, almost globose, most of the spikelets in contact with the spikelets of adjacent branches; branch axes extending beyond the distal spikelets as 1-1.5 mm points. Spikelets 3.5-5 mm, with 2-5 florets. Glumes strongly keeled; lower glumes 1-2 mm, ovate, acute; upper glumes 1.5-3 mm, oblong-elliptic, acuminate, awned, awns 0.5-2.5 mm; lemmas 3-4.3 mm, ovate, keels scabrous, 1-veined, veins excurrent about 0.5 mm, apices acuminate to mucronate; paleas shorter than the lemmas; anthers 0.2-0.8 mm, pale-yellow. Seeds about 1.2 mm long, about 0.7 mm wide, transversely rugose, brown. 2n = unknown.
Distribution
Ariz., Fla., Mass., S.C.
Discussion
Dactyloctenium radulans has been found at few locations in the Flora region, most of which were associated with wool waste. It is native to Australia, where it is regarded as a valuable ephemeral pasture grass in the drier inland areas but also as a garden weed. It resembles Dactyloctenium aristatum Link of tropical eastern Africa, differing primarily in having transversely rugose, rather than granular, caryopses.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
"decumbent" is not a number.