Sphagnum pulchrum
Bot. Centralbl. 82: 42. 1900,.
Plants moderate-sized to robust, often quite dense and compact; green, brownish green, golden brown to dark-brown; capitulum flattopped and not especially 5-radiate. Stems green to dark-brown; superficial cortex of 2 layers of enlarged, moderately differentiated cells. Stem-leaves triangular to triangular-lingulate, 0.9–1.1 mm; appressed to spreading; apex apiculate, acute or narrowly obtuse, appressed to spreading; hyaline cells nonseptate and efibrillose. Branches straight to more typically curved, typically stout and blunt ended; strongly 5-ranked, leaves not much elongate at distal end. Branch fascicles with 2 spreading and 2 pendent branches. Branch stems green but often reddish at proximal end, with cortex enlarged with conspicuous retort cells. Branch leaves ovate to ovatelanceolate, 1.4–1.8 mm; straight to often subsecund; weakly undulate and slightly recurved; hyaline cells on convex surface with 1 pore per cell at apical end of cell, on concave surface with round wall-thinnings in the cells ends and angles; chlorophyllous cells triangular to triangular-ovate in transverse-section, very well-enclosed within concave surface. Sexual condition dioicous. Spores 25–28 µm; roughly papillous on both surfaces; proximal laesura more than 0.5 the length of the spore.
Habitat: Abundant in poor fens and raised bogs, forming dense carpets at water level, especially on floating mats
Elevation: low to moderate elevations
Distribution
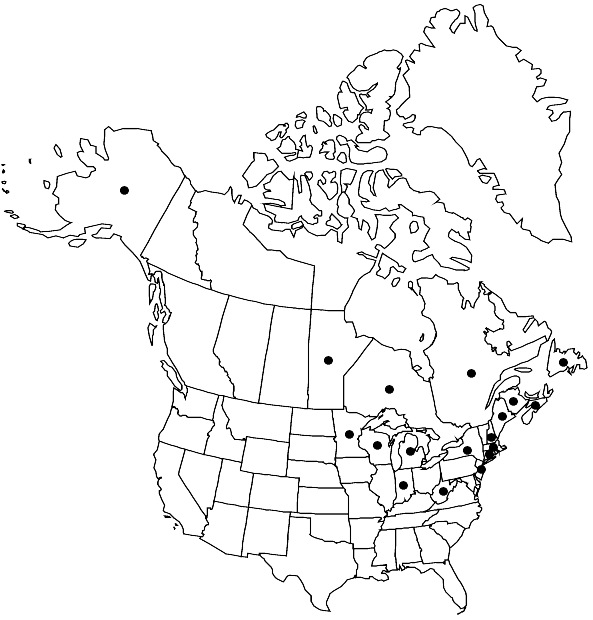
Man., N.B., Nfld. and Labr. (Nfld.), N.S., Ont., Que., Alaska, Conn., Ind., Maine, Mass., Mich., Minn., N.H., N.J., N.Y., Wis., W.Va., Europe
Discussion
Sporophytes are uncommon in Sphagnum pulchrum. With its distinctive broad and strongly 5-ranked branch leaves, It is one of our most easily recognized species.
Selected References
None.