Ditrichum
Flora 50: 181. 1867,.
| Taxon | Illustrator ⠉ | |
|---|---|---|
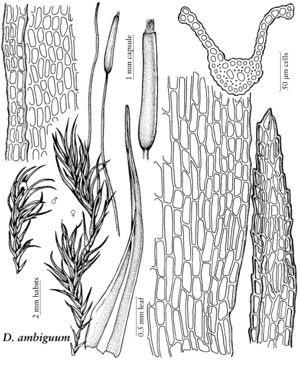 | Ditrichum ambiguum | Patricia M. Eckel |
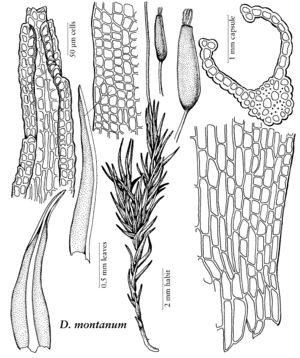 | Ditrichum montanum | Patricia M. Eckel |
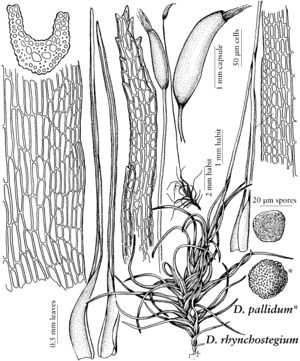 | Ditrichum pallidum Ditrichum rhynchostegium | Patricia M. Eckel Patricia M. Eckel |
Plants in loose to dense tufts, green to yellowish green distally, yellowbrown to brown proximally. Stems short or reaching 2 cm or more, simple or sometimes with a few branches; rhizoids at base, smoth. Leaves rigid to flexuose or sometimes somewhat falcate when dry, erect-spreading when wet, lanceolate to subulate from a more or less sheathing base; margins entire throughout or denticulate near the apex; costa percurrent or excurrent, occupying most of subula, 1/6–1/3 width of leaf base, 1 row of guide cells, 2 stereid bands, adaxial stereid band sometimes weak, rarely absent; medial lamina cells quadrate to shortrectangular, becoming longer and thinner-walled proximally toward margins, smooth or rarely papillose at both ends. Specialized asexual reproduction occasionally by rhizoidal tubers. Sexual condition monoicous or dioicous; perichaetial leaves usually with a longer and more or less sheathing base and shorter subulate than stem-leaves. Seta pale-yellow to dark reddish-brown, elongate, erect or flexuose. Capsule mostly erect and symmetric, sometimes ± inclined and arcuate, exserted, ovoid to cylindric, smooth; annulus present, deciduous; operculum conic to short-rostrate; peristome single, teeth16, split into 2 filiform segments or sometimes irregularly perforate or split, with or without a short basal membrane, papillose to spiculose. Calyptra cucullate. Spores globose, very finely papillose, verrucose, or with somewhat vermicular ornamentation.
Distribution
Worldwide, including maritime Antarctic region
Discussion
Species ca. 90 (11 in the flora).
Ditrichum occurs from near sea level up to montane regions, on a wide range of soils, but is found occasionally on rock; some species are calciphilic.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
Key
| 1 | Plants densely tufted, stems ± tomentose proximally | > 2 |
| 1 | Plants loosely to densely tufted or gregarious; stems, if tomentose, only so at extreme base | > 3 |
| 2 | Stems 1-4 cm; leaves to 3 mm, from an ovate-sheathing base sharply contracted to the subula; costa abaxially strongly convex; lamina cells near costa with weakly nodulose longitudinal walls; plants commonly fruiting. | Ditrichum flexicaule |
| 2 | Stems to 7 cm or more; leaves from an elongate-ovate base tapering gradually to the long slender subula; costa abaxially weakly convex; basal laminal cells with weakly to strongly nodulose longitudinal walls; rarely found fruiting | Ditrichum gracile |
| 3 | In cross section, distal leaf lamina partially 1-stratose with 2-stratose margins | > 4 |
| 3 | In cross section, distal leaf lamina 2-stratose from costa to margins | > 8 |
| 4 | Leaves erect-appressed to erect-patent when moist | > 5 |
| 4 | Leaves erect-spreading when moist | > 6 |
| 5 | Leaves oblong-lanceolate, widest proximally to middle, tapering to a blunt apex; lamina cells thin-walled, rectangular throughout, slightly shorter and narrower towards apex; seta to 2.5 cm, yellowish to orange-brown, erect; peristome teeth 200-220 µm, perforate, divided into 2 adhering filaments, finely papillose. | Ditrichum lineare |
| 5 | Leaves lanceolate to linear-lanceolate, gradually acuminate; lamina cells ± incrassate, subquadrate to short-rectangular distally, elongate-rectangular proximally; seta to 1.5 cm, reddish with age; peristome teeth 200-250 µm, the filaments finely and obliquely ridged and lightly papillose. | Ditrichum pusillum |
| 6 | Stems fastigiately branched from base, dichotomous distally; leaves linear-lanceolate, margins subserrulate distally, apex coarsely toothed; seta to 2.5 cm, pale yellow; capsule straight and erect or slightly curved, orange- to dark red-brown at maturity, elliptical, narrowed at mouth, 2-3 mm, flattened when dry; peristome teeth 600-800 µm, spiculose-papillose; autoicous. | Ditrichum montanum |
| 6 | Stem branching distally from base; leaves lanceolate to linear-lanceolate, margins entire to serrulate distally, apex weakly toothed; seta shorter, 0.8-2 cm, red to orange-brown; capsule symmetric to slightly curved, 1-3 mm, not flattened when dry; peristome teeth 200-500 µm, papillose to spiculose; dioicous | > 7 |
| 7 | Stems to 2 cm, often branched; leaves 1.5-4.5 mm, apex entire or serrulate, margins broadly recurved from base to leaf middle; leaf cross section 2-stratose on margins and sometimes near costa; seta 1.5-2 cm, red; capsule usually symmetric, straight and erect, rarely curved, 1.5-3 mm long, dark brown to reddish; peristome teeth 200-500 µm, twisted when dry. | Ditrichum ambiguum |
| 7 | Stems to 0.5 cm, seldom branched; leaves 1-3 mm, apex serrulate, margins plane or narrowly recurved from above leaf base to leaf middle; leaf cross section 2-stratose only at or near margins; seta 0.8-1.2 cm, orange-yellow, brownish or reddish; capsule usually asymmetric, erect, curved, 1-2 mm, yellow or light brown; peristome teeth 200 µm, nearly straight. | Ditrichum tortuloides |
| 8 | Stem leaves 1.5-3 mm, from an ovate to oblong base gradually tapered to a channelled subula, erect-patent to subsecund; dioicous. | Ditrichum heteromallum |
| 8 | Stem leaves longer, 3-7 mm, long-subulate from an ovate to short-rectangular base, spreading, flexuose to subsecund; autoicous | > 9 |
| 9 | Leaves to 5 mm; seta to 2.5 cm, orange-yellow, becoming reddened at maturity; capsule ovoid-cylindric, ± asymmetric and slightly curved, pale brown, suberect, flattened when dry; peristome teeth to 1500 µm, densely spiculose-papillose; spores yellow-brown, 11-19 µm, vermicular papillose-verrucose | Ditrichum rhynchostegium |
| 9 | Leaves 3-7 mm; seta 1-3 cm, yellow or becoming reddish brown at the base when mature; capsules subcylindric to cylindric, not flattened when dry; peristome teeth to 800 µm, finely papillose to spiculose-papillose; spores brown, 15-30 µm, coarsely roughened-papillose | > 10 |
| 10 | Leaves long-subulate from a short-ovoid sheathing base; seta to 2.5 cm, yellow, becoming reddened at the base with maturity; capsule suberect, subcylindric, 1-2.5 mm; peristome teeth pale brown to orange-brown, 300-800 µm, spiculose- papillose; spores 15-30 µm. | Ditrichum pallidum |
| 10 | Leaves narrow filiform-subulate from an ovate-lanceolate sheathing base; seta 1-3 cm, yellow; capsule cylindric, 1.5-3 mm; peristome teeth pale yellow-brown, to 300 µm, irregularly perforate, finely papillose; spores 20-30 µm. | Ditrichum schimperi |