Saelania
Utkast Eur. Bladmoss., 35. 1878 ,.
| Taxon | Illustrator ⠉ | |
|---|---|---|
 | Saelania glaucescens | Patricia M. Eckel |
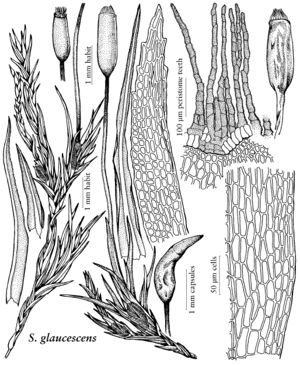
Plants tufted, glaucous bluish green or sometimes yellowish green. Stems short or reaching 1.5 cm, simple or branched; rhizoids at base, papillose or smooth. Leaves somewhat flexuose or contorted when dry, narrowly lanceolate, gradually acuminate, margins plane or narrowly recurved and entire proximally, irregularly and often doubly toothed or serrate distally; costa 1, percurrent to short-excurrent, 1/5–1/3 width of leaf base; medial laminal cells smooth subquadrate to shortrectangular, smoth. Specialized asexual reproduction unknown. Sexual condition autoicous; perigonia terminal on well-developed branches; perichaetial leaves not differentiated. Seta yellow or yellowbrown, elongate, erect. Capsule erect and symmetric, exserted, yellowbrown, cylindric, ± longitudinally plicate when dry and empty; annulus of 2–3 rows of large, pale cells, persistent; operculum rostrate; peristome single, teeth16, split into 2 filaments, densely papillose. Calyptra cucullate. Spores globose, finely papillose.
Distribution
North America, Europe, Asia, Africa, Pacific Islands (Hawaii), Pacific Islands (New Zealand)
Discussion
Species 1.
Saelania is morphologically close to Ceratodon, but differs in having the leaves a glaucous blue-green; seta yellow to yellow-brown; capsule yellow-brown, erect, and somewhat plicate but not strongly sulcate when dry; peristome reddish brown, densely papillose, divided to near the base into two unbordered filaments; and spores greenish to yellowish brown and larger, 15–20(–22) µm. In Ceratodon the leaves are yellowish green to brownish or reddish green; seta reddish to purplish; capsules dark reddish brown to purplish, erect to inclined or horizontal, and when dry usually strongly sulcate; peristome teeth dark red, papillose, divided to near the base into 2 filiform segments with pale borders and the segments often united at the nodes; and spores yellow to greenish yellow, and smaller (10–15 µm).
Selected References
None.