Didymodon nigrescens
J. Hattori Bot. Lab. 39: 510. 1975,.
Plants usually red to black-brown, occasionally yellow or orangebrown at apex. Stems 1.5–2.3 cm, central strand absent or present. Stem-leaves appressed when dry, spreading and not keeled when moist, monomorphic, long-ovate to lanceolate, broadly concave adaxially across leaf, usually 0.8–1.7 mm, base weakly differentiated in shape, long-ovate, margins usually broadly recurved to revolute to mid leaf or to near apex, minutely crenulate, apex acute to narrowly acuminate, often weakly cucullate; costa percurrent or ending 2–4 cells below the apex, little tapering, not strongly spurred, without an adaxial pad of cells, adaxial costal cells rectangular, 2 cells wide at mid leaf grading to 4 below, guide cells in 1 layer; basal laminal cells differentiated medially, walls thick, rectangular, not perforated; distal laminal cells in rows, 7–11 (–14) µm wide, 1: 1 or often longitudinally elongate, papillae apparently absent but visible in section as low, flattened to multiplex capitulate lenses, 1–3 per lumen, lumens ovate, walls evenly thickened and weakly convex on both sides of lamina, 1-stratose. Specialized asexual reproduction absent. Seta 0.7–0.9 cm. Capsule 1.5–2.8 mm; peristome teeth 32, linear, straight to twisted 1.5 times, 100–600 µm. Spores 9–13 µm. Distal laminal KOH reaction red.
Phenology: Capsules mature spring–fall.
Habitat: Limestone, frostboils, outcrops, cliff faces, often near streams and waterfalls
Elevation: low to moderate elevations (0-700 m)
Distribution
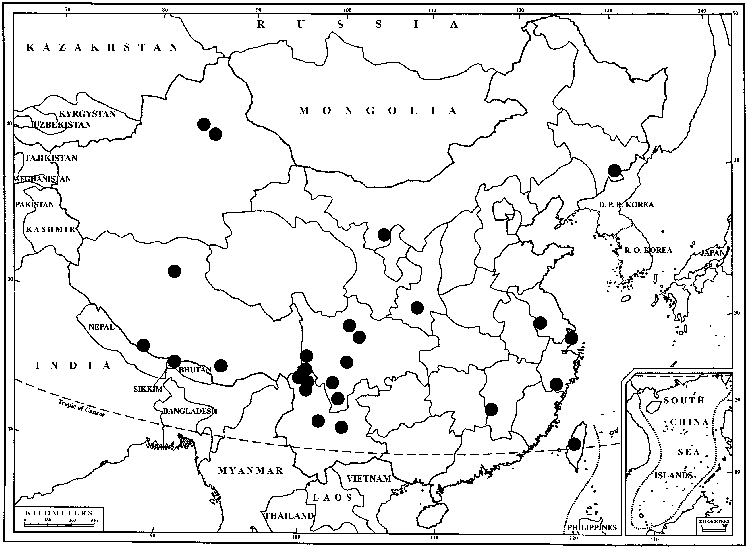
B.C., N.W.T., Alaska, Central America (Guatemala), e Asia
Discussion
The specimens cited as Didymodon nigrescens from the Firth River Basin by W. C. Steere (1978), determined by R. H. Zander, are actually Didymodon subandreaeoides. The distinguishing characters of D. nigrescens are the blackish coloration when dry (red in KOH), thin costa and distal laminal margins minutely crenulate by the small, bulging marginal cells. This and the following two species appear to be closely related by the rather distinctive crenulation of the leaf apices. Didymodon asperifolius is similar but may be distinguished by its longer leaves, straight or reflexed to strongly recurved when wet, distal margins recurved and smooth, distal laminal cells larger, 10–13 µm wide, epapillose or papillae simple, costa usually rather wide.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
"um" is not declared as a valid unit of measurement for this property."um" is not declared as a valid unit of measurement for this property."um" is not declared as a valid unit of measurement for this property.