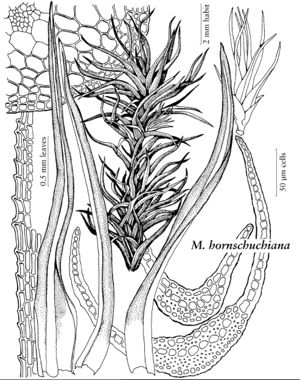
Molendoa hornschuchiana
Laubm. Deutschl. 1: 248. 1886,.
Stems to 2 cm, sclerodermis present. Leaves longlanceolate, 3–4 mm, proximal shoulders denticulate by projecting corners of marginal cells, apex subulate; leaf base much widened, ovate-rectangular, sheathing the stem; costa excurrent as a mucro, semilunar in section at mid leaf, guide cells 4–9; distal laminal cells often longitudinally elongate medially, 1–2: 1, rarely 2-stratose in patches.
Habitat: Mesic, quartzitic-slatey outcrops
Elevation: low evelations (100-150 m)
Distribution
Alaska, c Europe, Asia, n Africa
Discussion
Mesic, quartzitic-slatey outcrops; low evelations (100–150 m); Alaska; c Europe; Asia; n Africa.
Molendoa hornschuchiana is known (R. H. Zander 1979b) from only one site in the flora area, in southern Alaska (Valdez Area, Chugach Mountains, between Delta Junction and Valdez, Keystone Canyon, alongside Hwy. 4, near Bridal Veil Falls). This distinctive species is the largest of the genus, with stems reaching several centimeters in European specimens seen, and perichaetial leaves to 3 mm. The Alaskan material lacks sporophytes but has lateral perichaetia. Worldwide, the species is disjunctive between mountainous areas with high annual precipitation in temperate climates.