Philonotis calcarea
Coroll. Bryol. Eur., 86. 1856.
Plants large, in loose or occasionally compact tufts, bright green to yellowish, brownish proximally. Stems 4–8 cm, erect, simple, tomentose proximally. Leaves not or rarely seriate or spiraled, appressed on sterile and female stems, secund when dry, erect-spreading to falcate spreading when moist, ovatelanceolate to lanceolate, 1.3–3 mm; margins revolute, serrulate nearly throughout, teeth paired on mature leaves; apex evenly and gradually acuminate; costa subpercurrent to short-excurrent, 600 µm wide at base, distal abaxial surface weakly prorulose; laminal cells prorulose at proximal ends; basal-cells rectangular, shorter, broader than distal; juxtacostal cells at widest part of leaf 48–100 µm; distal cells linear, 20–40 × 3–5 µm. Specialized asexual reproduction absent. Sexual condition dioicous; perigonia discoid. Seta 4 cm, straight or flexuose. Capsule 2–3.5 mm. Spores subreniform, 22–25 µm.
Habitat: Moist areas
Elevation: low to moderate elevations
Distribution
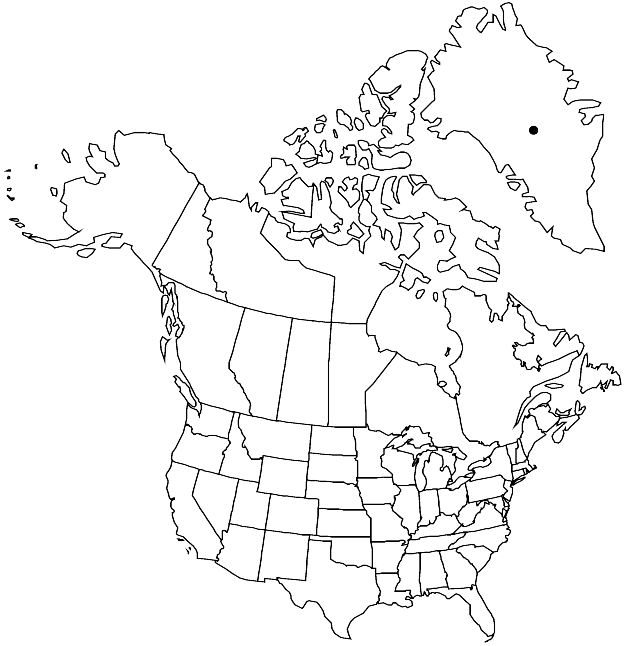
Greenland, Europe, Asia, Africa
Discussion
Philonotis calcarea is a member of the P. fontana complex; it is essentially an Old World species that enters the flora area only in southern Greenland. Its distinguishing features include falcate-secund, plicate leaves, very stout costa, and lax, pellucid, and quite large juxtacostal cells.
Selected References
None.