Mnium arizonicum
Rev. Bryol. 52: 23. 1925.
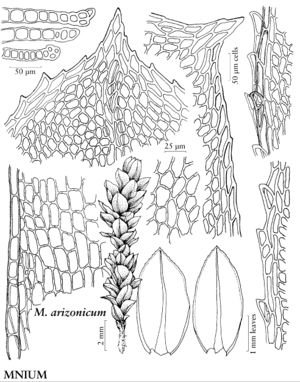
Plants 1–2 (–4) cm. Stems reddish-brown or dark red. Leaves pale to dark green, usually contorted and spirally twisted when dry, obovate, elliptic, or sometimes obovate-spatulate, 2.5–3.5 (–4.5) mm; base short or rarely long-decurrent; margins green, 1-stratose or 2-stratose, toothed in distal 1/3 of leaf, rarely to below mid leaf or entire, teeth paired or single, small, blunt, sometimes indistinct, occasionally long and sharp; apex acute or rounded-acute, apiculate or rarely cuspidate, cusp toothed; costa percurrent or occasionally subpercurrent, distal abaxial surface smooth or toothed; medial laminal cells elongate or sometimes oblong, (20–) 25–40 (–50) µm, smaller near margins, in diagonal, sometimes longitudinal rows, weakly or not collenchymatous, walls pitted, blue postmortal color absent; marginal cells short-linear or rhomboidal, sometimes mixed with linear cells, in 2 or 3 rows. Sexual condition dioicous. Seta single. Capsule yellowbrown, 2–3 (–4) mm; operculum rostrate, rostrum strongly bent when dry; exostome brown, sometimes dark reddish-brown. Spores 15–24 µm.
Phenology: Capsules mature summer.
Habitat: Damp soil, humus, rock, shaded cliffs
Elevation: low to high elevations
Distribution
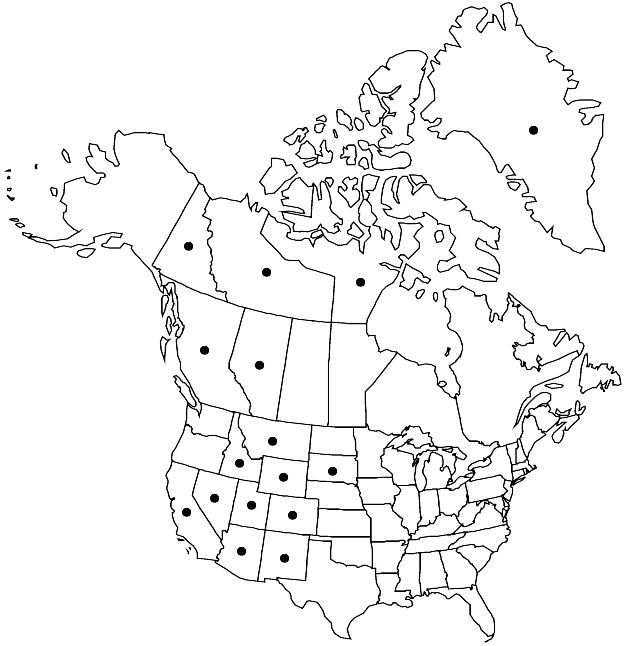
Greenland, Alta., B.C., N.W.T., Nunavut, Yukon, Ariz., Calif., Colo., Idaho, Mont., Nev., N.Mex., S.Dak., Utah, Wyo.
Discussion
Mnium arizonicum is distinguished by its small size, elongate and pitted laminal cells (this is the only species of Mnium with pitted cell walls) often in distinct rows, and leaf margins composed in large part of short-linear and oblong cells with small, often single and blunt teeth. S. Flowers (1973) observed that the marginal teeth can vary widely on leaves of a single shoot, with some leaves entire and others with paired teeth.
Selected References
None.