Mnium spinulosum
Bryol. Europ. 4: 206, plate 394. 1846.
Plants 0.5–1 (–2.5) cm. Stems red or reddish-brown. Leaves green to dark green, slightly contorted or undulate when dry, obovate or occasionally elliptic, 2.5–5 mm; base long-decurrent; margins reddish-brown, multistratose with stereid band, toothed distally, teeth paired, long, sharp; apex acute, obtuse, or rounded-acute, cuspidate, cusp toothed; costa percurrent or excurrent, distal abaxial surface smooth, sometimes with few small teeth; medial laminal cells ± isodiametric or short-elongate, 25–40 µm, smaller towards margins, not in rows, not collenchymatous, blue postmortal color absent; marginal cells linear, in (3–) 4–5 rows. Sexual condition synoicous. Seta single or multiple. Capsule pale-yellow, 1.5–4 mm; operculum rostrate; exostome dark reddish-brown, often purplish. Spores 16–24 µm.
Phenology: Capsules mature late spring.
Habitat: Forests, on humus, logs, rock, base of trees
Elevation: low to moderate elevations
Distribution
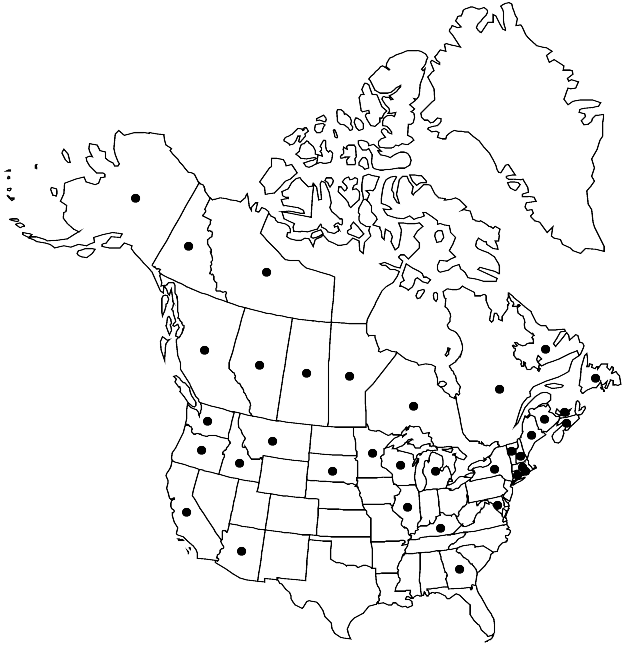
Alta., B.C., Man., N.B., Nfld. and Labr., N.W.T., N.S., Ont., P.E.I., Que., Sask., Yukon, Alaska, Ariz., Calif., Conn., Ga., Idaho, Ill., Ky., Maine, Md., Mass., Mich., Minn., Mont., N.H., N.Y., Oreg., R.I., S.Dak., Vt., Wash., Wis., Europe, Asia
Discussion
Mnium spinulosum is distinguished by usually obovate leaves with broad, thick, and pigmented margins, and dark reddish brown exostomes. The capsule mouths are dark reddish brown; H. A. Crum and L. E. Anderson (1981) referred to this species as the red-mouthed mnium.
Selected References
None.