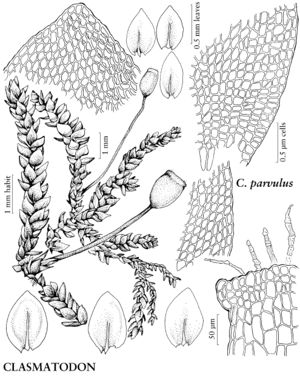
Clasmatodon parvulus
in A. Gray, Manual ed. 2, 660. 1856.
Plants slender, in interwoven mats. Stems to 1 (–2) cm, branches to 2 (–5) mm, erect; axillary hair distal cell obtuse, pale-brown. Stem-leaves ± subsecund, 0.3–0.5 mm wide; laminal cells 18–30 × 8–10 µm, smooth. Seta 0.2–0.5 cm. Capsule 0.7–1 mm; annulus 3-seriate or 4-seriate, cells small, brown; exostome teeth blunt, partially connate; endostome basal membrane inconspicuous, segments 16, short, slender, unequally 2-fid, partially fused to basal membrane. Spores finely roughened.
Habitat: Tree trunks and bases, flood plain forests, calcareous rock
Elevation: low to moderate elevations (0-400 m)
Distribution
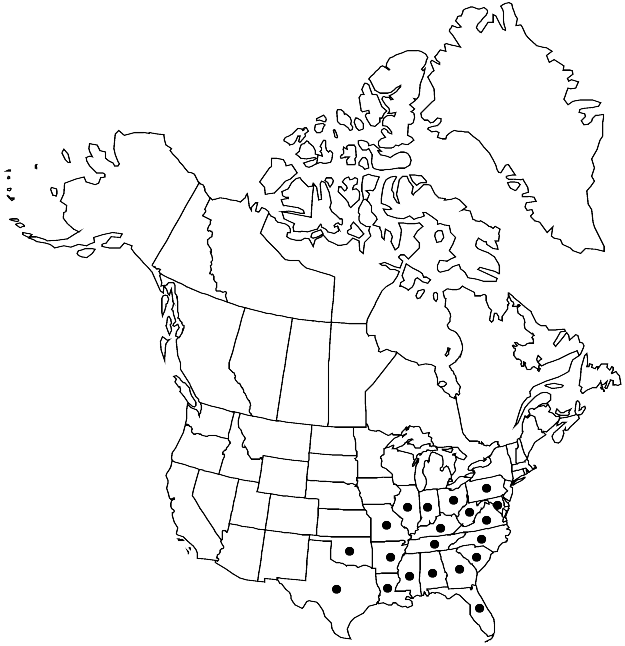
Ala., Ark., Fla., Ga., Ill., Ind., Ky., La., Md., Miss., Mo., N.C., Ohio, Okla., Pa., S.C., Tenn., Tex., Va., W.Va., Europe
Discussion
The inconspicuous plants of Clasmatodon parvulus form small, slender, straggly mats on tree trunks in southeastern North America north of Mexico. The species is characterized by a short costa (Leskea species have a strong costa ending near the apex), ovate, mostly bluntly acute leaves (Lindbergia has long-acuminate leaves), and a lack of erect, flagelliform branchlets (as in Platygyrium repens). The elliptic, erect capsules with a reduced peristome on short setae also are diagnostic.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
"long" is not a number."broad" is not a number.