Fatoua villosa
Bot. Mag. (Tokyo) 4: 516. 1927.
Herbs, to ca. 8 dm. Stems erect, branched, pubescent with hooked trichomes. Leaves: stipules linear to linear-lanceolate, 1.8-2.5 mm; petiole 1-6 cm, often ± as long as leaf-blade. Leaf-blade to 2.5-10 × 1-7 cm, papery, base cordate to truncate, margins crenate-dentate, apex acute to acuminate; surfaces abaxially and adaxially appressed-hirsute. Inflorescences cymes, dense, 4-8 mm wide, subtended by narrow bract; peduncle 1-2 cm. Flowers light green, staminate and pistillate in same cyme. Staminate flowers: calyx campanulate; stamens exserted. Pistillate flowers: calyx boatshaped; ovary globose, puberulent, somewhat depressed in axis; style reddish purple, filiform. Achenes white, oval, 3-angled, ca. 1 mm, minutely muricate, with 2 triangular, membranous appendages. Seeds explosively expelled.
Phenology: Flowering summer–fall.
Habitat: Disturbed sites
Elevation: 0-300 m
Distribution
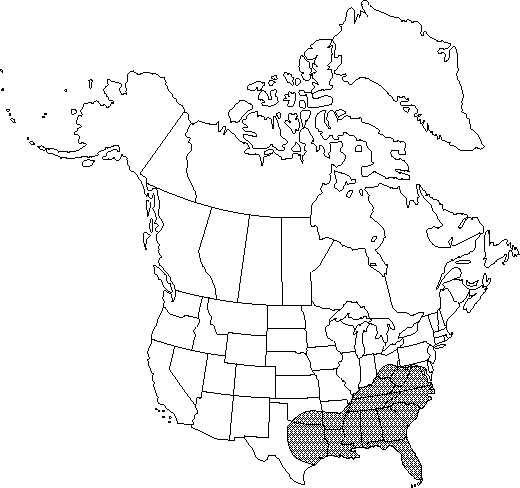
Introduced; Ala., Ark., Fla., Ga., Ky., La., Md., Miss., Mo., N.C., Ohio, Okla., S.C., Tenn., Tex., Va., W.Va., West Indies (Bahamas), native to Asia
Discussion
Fatoua villosa was first reported for North America from Louisiana by J. W. Thieret (1964). It has become widespread in the eastern and lower midwestern states where it often occurs as a weed in greenhouses and disturbed sites. Apparently it spreads from the distribution of horticultural materials.
Selected References
None.
