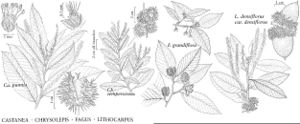
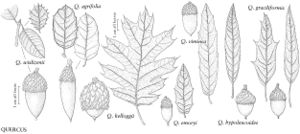
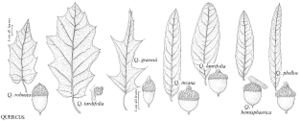
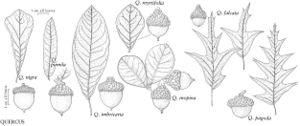
Fagaceae
Trees or shrubs, evergreen or deciduous, shrubs sometimes rhizomatous. Winter buds sessile, with few-to-many imbricate scales (2 valvate scales enclosing imbricate scales in Castanea); terminal bud present or absent. Leaves alternate, spirally arranged, simple; stipules deciduous (usually), distinct, scarious; petiole present. Leaf-blade lobed or unlobed, pinnately veined, margins serrate, dentate, or entire; surfaces usually pubescent, at least when young, sometimes with scales. Inflorescences unisexual or androgynous catkins; staminate and androgynous catkins spicate or capitate, rigid, flexible, or lax, consisting of few to many-flowered clusters, bracts present or absent; pistillate catkins rigid or flexible, with 1-several spicately arranged, rarely solitary, terminal cupules bearing 1-3 (-15 or more) pistillate flowers. Staminate flowers bracteate, bracts often caducous; sepals (3-) 4-6 (-8); stamens (3-) 6-12 (-18 or more); petals absent; anthers 2-locular, dehiscing by longitudinal slits, pollen-sacs contiguous; pistillode often present and indurate, or vestigial as central tuft of trichomes. Pistillate flowers: calyx of 4-6 distinct or connate sepals; petals absent; pistil 1, 3 (-6 or more) -carpellate; ovary inferior, locules as many as carpels; placentation axile; ovules pendulous, 2 in each locule, all but 1 in each pistil usually aborting; styles as many as carpels, distinct to base; stigmas dry; staminodes present or absent. Fruits nuts, sometimes winged, 1-seeded, subtended or enclosed individually or in groups of 2-3 (-15) by scaly or spiny, multibracteate cupule; seed-coat membranous; endosperm none; embryo straight, as long as seed; cotyledons fleshy, starchy or oily.
Distribution
Widespread, often dominant forest trees in temperate, subtropical, and tropical areas, mostly Northern Hemisphere
Discussion
Genera 9, species probably 600-800 (5 genera, 97 species, and numerous hybrids in the flora).
In the Western Hemisphere, Fagaceae are found from southern Canada to Colombia; they are absent or infrequent in most of the northern Great Plains and northern Rocky Mountain region.
Fagaceae are one of the most important families of Northern Hemisphere woody plants in terms of total biomass and economic use. They are widely used for lumber, firewood, and horticultural plantings; the nuts are often used for animal fodder and, in some species, for human food (particularly Castanea). As dominants in forests, woodlands, and chaparral, native stands of fagaceous trees and shrubs provide optimal wildlife habitat, often harboring an exceptionally diverse insect fauna. Most of the diversity of the family in the Western Hemisphere is concentrated in the genus Quercus, with the greatest number of species in Mexico (at least 125 species), and a secondary area of diversity in the southeastern United States.
Polyploidy has not been reported in any natural populations of species of Fagaceae. Natural interspecific hybridization is common in the family, particularly in Quercus, and also in Castanea and Lithocarpus.
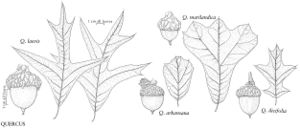
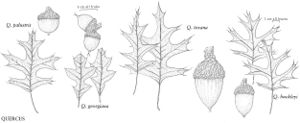
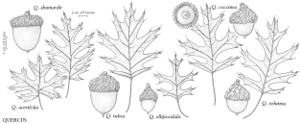
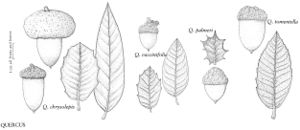
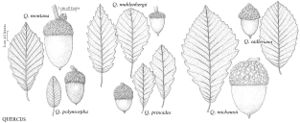
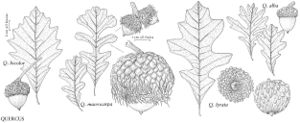
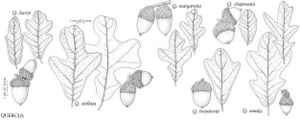
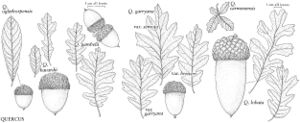
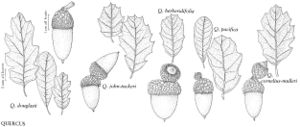
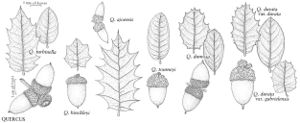
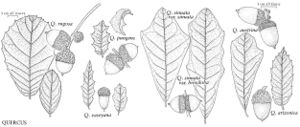
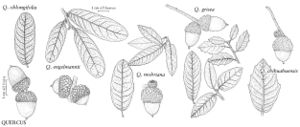
The most important diagnostic feature of Fagaceae is the cupule, which occurs as the cup or cap of the acorn in Quercus and Lithocarpus and the spiny bur that surrounds the fruits of Castanea and Chrysolepis. The cupule is sometimes referred to as an involuc involucre, however, is made up of bracts, while the cupule has been shown to be a complex structure that is interpreted as an indurated, condensed, partial inflorescence formed by fusion of stem axes with several orders of branching, bearing bracts that are modified as scales and/or spines (see B. S. Fey and P. K. Endress 1983).
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
Illustrations
Key
| 1 | Fruits acorns, acorn a solitary nut, circular in cross section, at least partially covered by scaly cup, cup unlobed, without visible sutures or valves; scales not noticeably spinose; nut not completely enclosed by cup at maturity (except in Quercus lyrata). | > 2 |
| 1 | Fruits of 1-several nuts, nut usually 3-angled or rounded-angular in cross section, enclosed in spiny or prickled cupule; cupule valves 2-4(-8+), distinct or marginally connate along sutures, these ±completely enveloping nut(s) until maturity. | > 3 |
| 2 | Cup scales strongly reflexed, hooked at tip; staminate and androgynous inflorescences erect or ascending, rigid or flexible, often appearing terminal and branched | Lithocarpus |
| 2 | Cup scales various, or if somewhat reflexed (rarely), then not noticeably hooked at tip; staminate inflorescences lax, axillary or clustered near base of new growth; androgynous inflorescences absent | Quercus |
| 3 | Spines/scales of cupule unbranched, stout, not obscuring surface of cupule; inflorescences unisexual (staminate below pistillate on same branch); pistillate flowers (and fruits) typically 2 per cupule; staminate inflorescences lax, loosely capitate; nut sharply angular, slightly winged | Fagus |
| 3 | Spines of cupule branched, interlocking and usually obscuring surface of cupule; inflorescences staminate and androgynous (staminate below androgynous on same twig); pistillate flowers (and fruits) 1-3 or many per cupule (rarely but not consistently 2); staminate inflorescences spicate, rigid or flexible; nut angular or rounded, not winged. | > 4 |
| 4 | Plants evergreen; leaves thick, leathery, margins entire (rarely spinose in sprouts), secondary veins obscure, not strongly parallel; adjacent nuts separated from each other by internal cupule valves; bud scales imbricate; spines of cupule without simple hairs, with large, yellowish, multicellular glands; styles | Chrysolepis |
| 4 | Plants winter-deciduous; leaves thin, somewhat leathery, secondary veins prominent, parallel, ending in prominent marginal teeth or awns; adjacent nuts not separated by cupule valves within cupule; buds with 2 unequal opposite outer scales that cover several imbricate inner scales; spines of cupule densely or sparsely with simple hairs; styles 6 or more | Castanea |