Aspicarpa hirtella
Mém. Mus. Hist. Nat. 2: 396, plate 13. 1815.
Plants erect, 10–20 cm, or decumbent, branches 10–60 (–100) cm. Leaves: petioles 1–3 mm; blade narrowly to broadly lanceolate or ovate, larger blades 15–45 × 6–23 mm, length 1.3–2.5 times width, base rounded or shallowly cordate, apex usually obtuse, occasionally acute, surfaces thinly sericeous or velutinous, hairs strongly appressed to V-shaped, more persistent abaxially than adaxially. Chasmogamous flowers in (2–) 4 (–7) -flowered umbels, occasionally corymbs, terminating leafy shoots; petals carrot yellow; staminodes equaling or longer than fertile stamens, surpassing sepals. Cleistogamous flowers often borne singly, or in clusters raised on slender axillary stalk, 5–55 mm, also sessile or subsessile in axils of full-sized leaves. Nutlet 3–3.5 mm diam., smooth or rugose, dorsal crest 0.5–0.8 mm, entire, extended forward 1–1.5 mm. 2n = 80.
Phenology: Flowering and fruiting (May–)Jul–Sep(–Oct).
Habitat: Dry rocky slopes among boulders, grassy slopes with oaks, pines, junipers.
Elevation: 1200–2000 m.
Distribution
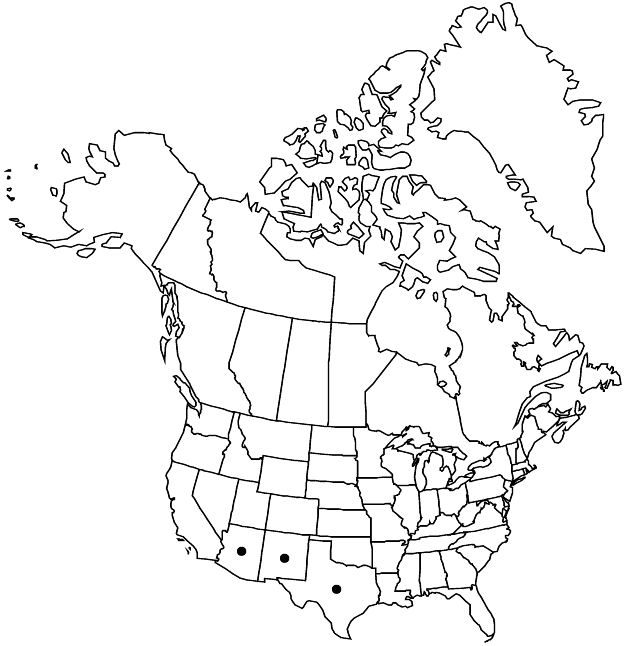
Ariz., N.Mex., Tex., Mexico
Discussion
In the flora area, Aspicarpa hirtella is restricted to southeastern Arizona, southwestern New Mexico, and trans-Pecos Texas.
Selected References
None.