Arceuthobium campylopodum subsp. abietinum
Phytoneuron 2012-51: 9. 2012.
Plants forming witches brooms. Stems yellow, green, olive green, orange, brown, or red, 8 (–22) cm; third internode 4–14 (–23) × 1.5–2 (–4) mm, dominant shoot 1.5–6 mm diam. at base. Staminate flowers 2.5 mm diam.; petals 3 (–4). Fruits 4 × 2 mm.
Phenology: Flowering Jul–Aug(–Sep); fruiting Sep–Oct.
Habitat: Coniferous forests generally with fir.
Elevation: 0–2700 m.
Distribution
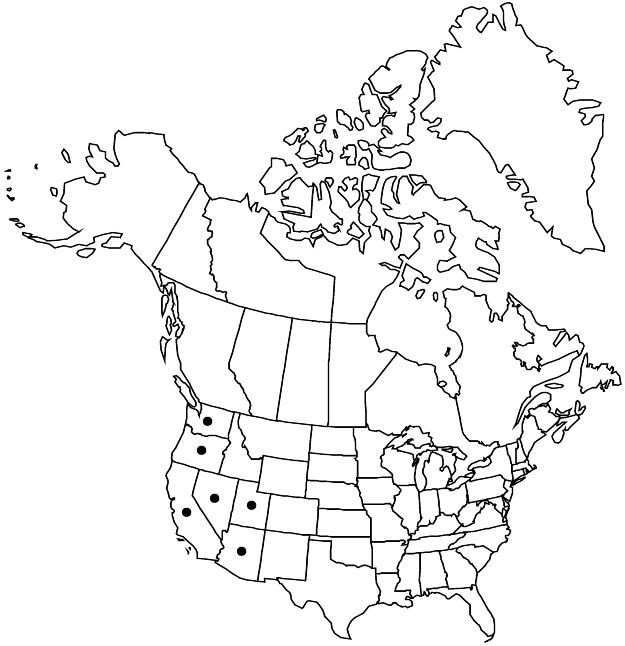
Ariz., Calif., Nev., Oreg., Utah, Wash., Mexico (Chihuahua)
Discussion
Meiosis occurs in July, with fruits maturing 13 to 14 months after pollination.
Subspecies abietinum includes forma speciales concoloris Hawksworth & Wiens, which parasitizes Abies concolor (white fir), and forma speciales magnificae Hawksworth & Wiens, which parasitizes A. magnifica (red fir). These forms were based upon inoculation studies showing that seeds of one form apparently will not infect the other's host species and vice versa (J. R. Parmeter and R. F. Scharpf 1963). Morphologically the two forms are extremely similar, with the former having a greater mean shoot height (10 versus 6 cm). The white fir dwarf mistletoe occurs throughout the above geographical range whereas red fir dwarf mistletoe is restricted to California and southwestern Oregon. In addition to the above two species of fir, Abies durangensis and A. grandis are principal hosts; secondary to rare hosts include A. lasiocarpa, Picea breweriana, Pinus ayacahuite, P. contorta, P. lambertiana, and P. monticola.
Selected References
None.