Lepidium tiehmii
Novon 12: 9. 2002.
Perennials; (caudex woody, to 1 cm diam., covered with persistent petiolar remains); glabrous throughout. Stems simple from base (caudex branch), erect, branched distally, 1–7.5 dm. Basal leaves rosulate; petiole (1.5–) 2.5–10 (–13) cm; blade oblong to lanceolate, (2.5–) 4.5–9 (–14) cm × 15–40 mm, margins entire. Cauline leaves shortly petiolate; blade oblanceolate, (much smaller than basal), base attenuate-cuneate, not auriculate, margins entire. Racemes (paniculate), considerably elongated in fruit. Fruiting pedicels divaricate-ascending, straight, (terete), 8–15 × 0.4–0.5 mm. Flowers: sepals oblong, 2.5–3 (–4) × 1.2–1.8 mm; petals creamy white to pale-yellow, obovate to oblanceolate, 4–5.5 (–6.5) × 2–3.3 mm, claw 1.5–2.2 mm; stamens 6; filaments (median pairs) 3.5–4.5 mm; anthers 1–1.2 mm. Fruits obovate to somewhat rhomboid, 7–11 × 5–6.5 mm, apically not winged, apical notch absent; valves thin, smooth, obscurely veined; style 0.2–0.6 mm. Seeds oblong, 3.7–4.5 × 1.6–2 mm.
Phenology: Flowering Apr–Jun.
Habitat: Rocky crevices and slopes in sagebrush communities
Elevation: 1400-1800 m
Discussion
Of conservation concern.
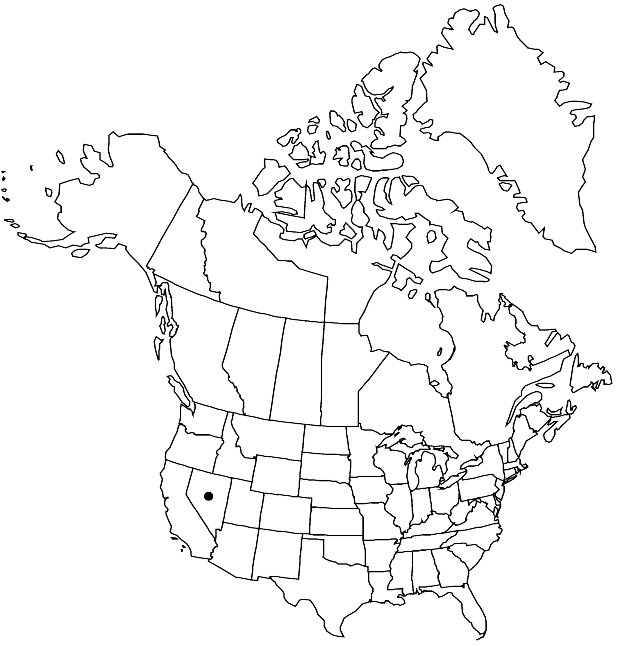
Lepidium tiehmii is known from mountain ranges in Douglas and Lyon counties. It was described and has been maintained (N. H. Holmgren 2005b) in Stroganowia, a genus now united with Lepidium (I. A. Al-Shehbaz et al. 2002) that otherwise is disjunct and restricted to the central Asian states of the Former Soviet Union and adjacent western China. In our opinion, the similarity of this species to those Asian ones formerly placed in Stroganowia is superficial and is the result of convergence rather than descent.
The cotyledonary type was erroneously reported as conduplicate (R. C. Rollins 1993; N. H. Holmgren 2005b). In the several seeds that we dissected it was always incumbent.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
"elongated" is not a number."thick" is not a number."dm" is not declared as a valid unit of measurement for this property.