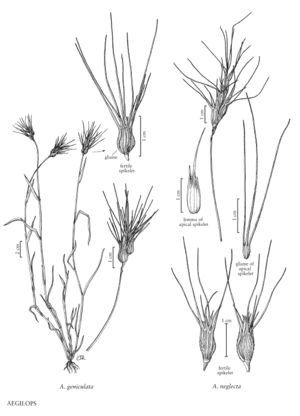
Aegilops geniculata
Culms 20-40 cm, geniculate at the base, usually with many tillers. Sheaths with hyaline margins, the distal portion of the lower cauline sheaths ciliate; blades 2-7.5 cm long, 2-5 mm wide. Spikes 1-3 cm long, bases 0.4-0.7 cm wide, narrowly ovoid to ellipsoid, gradually tapering distally, with (2) 3-4 spikelets, the distal spikelet sterile; rudimentary spikelets 1 (2); disarticulation at the base of the spikes, above the rudimentary spikelets. Fertile spikelets 7-10 mm long, 3-4 mm wide, urceolate; lower spikelet with 3-4 florets, the lower 1-2 florets fertile; apical spikelets 4-5 mm long, 1-2 mm wide, narrowly obovoid, with 1 floret, floret reduced, sterile. Glumes of fertile spikelets 6-10 mm, ovate, smooth, scabrous, appressed-velutinous, (3) 4 (5) -awned, awns 2-4.5 cm; glumes of apical spikelets about 3 mm, 4-awned, awns usually 1-3.5 cm; lemmas of fertile spikelets 6-8 mm, adaxial surfaces often velutinous distally, apices 2-3-awned, awns 1-2.5 cm. Caryopses 4-6 mm, falling free from the lemmas and paleas. Haplomes MU. 2n = 28.
Distribution
N.Y., Calif., Va.
Discussion
In the Flora region, Aegilops geniculata is known only from Mendocino County, California, where it usually occurs along roadsides. It is native from the Mediterranean area to central Asia. In California, it grows in silty clay.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
"decumbent" is not a number.