Antennaria geyeri
Mem. Amer. Acad. Arts, n. s. 4: 107. 1849.
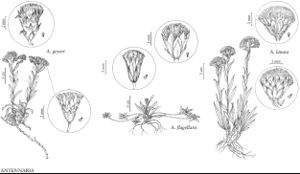
Dioecious. Plants 3–14 cm (bases woody). Stolons none. Basal leaves absent at flowering. Cauline leaves linear-lanceolate to cuneate-oblanceolate, 11–35 × 2–6 imm, acute, not flagged (apices acute), faces gray-pubescent. Heads 3–25 in corymbiform to paniculiform arrays. Involucres: staminate 6–8 mm; pistillate 6–8 mm. Phyllaries distally red to pink, light-brown, or white. Corollas: staminate 3–4.5 mm; pistillate 5–6 mm. Cypselae 2–2.5 mm, pubescent and papillate; pappi: staminate 6–7 mm (capillary); pistillate 6–7 mm. 2n = 28.
Phenology: Flowering summer.
Habitat: Dry lower montane to montane coniferous forests, usually in ± thick duff under Pinus ponderosa
Elevation: 600–2400 m
Distribution
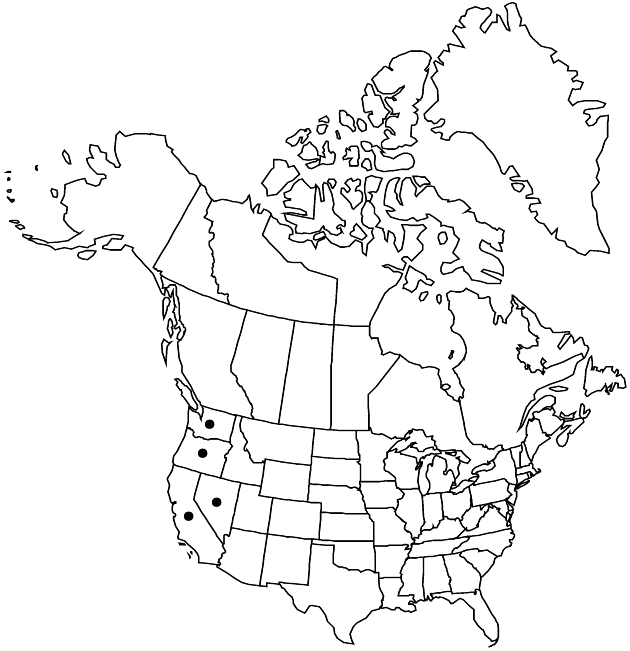
Calif., Nev., Oreg., Wash.
Discussion
Antennaria geyeri is distinctive because it has woody upright branches and is not stoloniferous. It lacks basal leaves at flowering and has heads that are often described as subdioecious (central flowers are often bisexual). As the only member of the Geyerae group, A. geyeri is not closely related to any other species of Antennaria; it bears strong similarities to some species of Anaphalis (R. J. Bayer 1990; Bayer et al. 1996).
Selected References
None.