Circaea
Sp. Pl. 1: 8. 1753.
| Taxon | Illustrator ⠉ | |
|---|---|---|
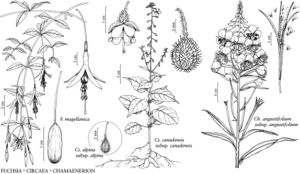 | Fuchsia magellanica Circaea canadensis subsp. canadensis Circaea alpina subsp. alpina Chamaenerion angustifolium subsp. angustifolium |
Herbs, perennial, caulescent, colonial; stolons numerous. Stems erect, unbranched or sparsely branched. Leaves cauline, opposite; stipules present, soon deciduous; petiolate; blade margins dentate to prominently dentate. Inflorescences simple or branched racemes, terminal on main-stem or also at apex of branches, erect. Flowers bisexual, zygomorphic, buds erect; floral-tube inconspicuous, deciduous (with sepals, petals, and stamens) after anthesis, with a nectary wholly within and filling proximal portion of floral-tube or elongated and projecting above opening of floral-tube as a fleshy, cylindrical or ringlike disc; sepals 2, reflexed to spreading; petals 2, alternate sepals, white or pink, without spots, clawed, apex notched; stamens 2, anthers basifixed, pollen shed singly; ovary 1-locular or 2-locular, stigma bilobed or obpyramidal, surface wet, minutely papillate. Fruit a capsule, spreading or slightly reflexed, globose to clavoid or obovoid, indehiscent, surface smooth or with prominent longitudinal grooves (sulci) and rounded ridges, burlike, with stiff, hooked hairs; pedicellate, deciduous at maturity. Seeds 1 or 2, ellipsoid, glabrous, without appendages. = 11.
Distribution
North America, Europe, Asia, n Africa
Discussion
Species 8 (3, including 1 hybrid, in the flora).
Circaea occurs throughout the temperate and boreal northern hemisphere, but is most diverse in eastern Asia, where all but one species occur. Reproductive features include: self-compatible; flowers diurnal, outcrossing, and pollinated by syrphid flies and small bees, or, sometimes, autogamous. It is found in rich, moist soils in deciduous forests and thickets, forest margins, and in moss or soil in mixed, coniferous-broadleaved deciduous, boreal forests. Circaea alpina subsp. alpina and C. canadensis subsp. canadensis often grow in close proximity and hybridize in eastern North America to produce C. ×sterilis. The unilocular C. alpina, with petals less than 2 mm, is self-pollinating under adverse weather conditions, but outcrosses on warm, sunny days. Because of its shorter style and much smaller pollen grains, it is probably the pollen recipient during hybridization events. Artificial hybridization experiments in England using C. alpina as the pollen donor and C. lutetiana as the pollen recipient failed to result in offspring, although hybrids were easily produced in the other direction (P. M. Benoit 1966). Recent molecular phylogenetic analysis supported the separation of the C. canadensis complex into two species; C. alpina subsp. pacifica was found to be sister to the remainder of the genus rather than being nested with other members of C. alpina (Xie L. et al. 2009). Thus, despite the strong morphological similarities of taxa within the C. canadensis and C. alpina complexes, these North American taxa may be better treated as separate species. Further detailed molecular studies are underway to examine this in more detail (Xie et al., unpubl.).
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
Key
| 1 | Flowers opening before elongation of raceme axis, clustered and corymbiform at apex of raceme, on ascending to erect pedicels; capsules clavoid, without corky ribs or grooves; stolons terminated by a tuber. | Circaea alpina |
| 1 | Flowers opening after elongation of raceme axis, more or less loosely spaced, borne on spreading pedicels; capsules usually obovoid to pyriform or subglobose, rarely clavoid, with corky, thickened ribs with deep grooves, or fruit sterile and aborting shortly after anthesis; stolons without or with a terminal tuber. | > 2 |
| 2 | Ovaries all or nearly all developing to maturity; capsules with corky thickened ribs separated by deep grooves; pollen highly fertile (greater than 80%); stolons without a tuber. | Circaea canadensis |
| 2 | Ovaries aborting shortly after anthesis, very rarely a few persistent, but easily detached, after anthesis; capsules, when somewhat persistent, smooth or with only low ribs and with shallow grooves; pollen highly sterile (less than 2% fertile); stolons terminated by a tuber or, more commonly, apex sligltly dilated. | Circaea ×sterilis |