Cirsium cymosum
Amer. Midl. Naturalist 30: 37. 1943.
Biennials or perennials, 25–120 cm, pubescence a mixture of fine, non-septate arachnoid trichomes and coarser, septate trichomes, especially along stems and on midveins on abaxial leaf faces, usually ± loose and irregularly deciduous from leaves in age; taprooted. Stems usually 1, erect, ± gray-tomentose, sometimes villous with septate trichomes; branches 0–10+, usually arising in distal 1/2, ascending, usually reaching a ± common height. Leaves: blades linear-oblong to oblanceolate or elliptic, 10–30 × 3–7 cm, shallowly to deeply pinnatifid with 3–8 pairs of lobes, longer than 2 cm, lobes well separated, linear to triangular-ovate, dentate to lobed proximally, main spines slender, 2–7 mm, faces green to gray, thinly to densely arachnoid-tomentose with fine, non-septate trichomes, sometimes villous with septate trichomes along veins, usually ± loose and irregularly deciduous from leaves in age; basal often present at flowering, sessile or winged-petiolate; principal cauline mostly in proximal 1/2, winged-petiolate or sessile, bases narrowed, auriculate, veins often prominently raised on abaxial faces; distal sessile, auriculate-clasping or short-decurrent 1–10 mm, progressively reduced becoming bractlike, often unlobed or less deeply divided and sometimes spinier than proximal. Heads borne singly, terminal on main-stem and branches, sometimes also in distal axils, erect, not subtended by well-developed leaves, collectively forming corymbiform or racemiform arrays. Peduncles (0–) 2–15 cm. Involucres ovoid to hemispheric or campanulate, 2–3 × 1.5–3.5 cm, ± arachnoid-floccose, often glabrate. Phyllaries in 8–10 series, subequal to strongly imbricate, green, linear to lanceolate (outer) to linear (inner), entire, abaxial faces with inconspicuous to prominent glutinous ridge; outer and mid bodies loosely spreading to ascending or appressed, apices subappressed to ascending or spreading, flat, spines ascending to spreading, fine, 2–4 mm; apices of inner commonly flexuous or reflexed, narrow, flat, scarious. Corollas creamy white to purplish, 20–31 mm, tubes 8–14 mm, throats 5.5–10 mm, lobes 6–7 mm; style tips 4–6 mm. Cypselae tan to dark-brown, 5–7.5 mm, apical collars not differentiated; pappi 16–25 mm.
Distribution
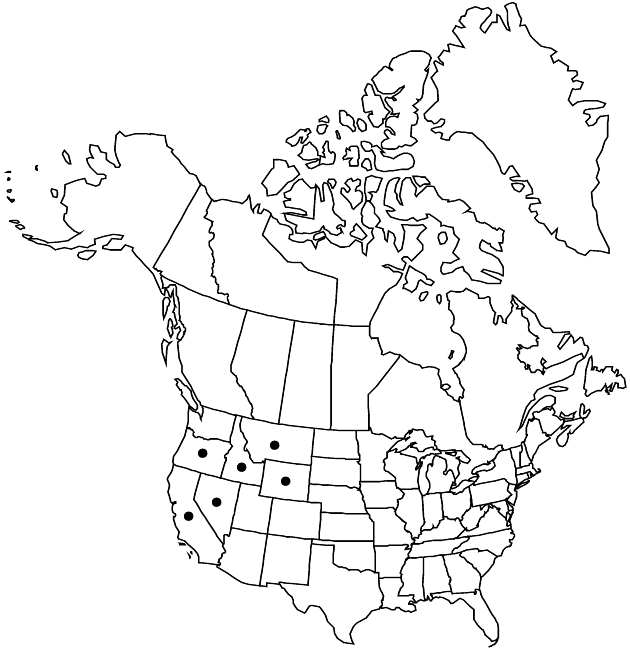
Calif., Idaho, Mont., Nev., Oreg., Wyo.
Discussion
Varieties 2 (2 in the flora).
Past floras have treated Cirsium cymosum and C. canovirens as separate species. In my examination of these plants across their combined ranges I realized that they are connected by numerous intermediates and that I could find no characters that consistently distinguish them.
Selected References
None.
Key
| 1 | Larger heads 20–35 mm diam.; outer phyllaries elongate, often nearly as long as inner; glutinous ridge narrow, weakly developed | Cirsium cymosum var. cymosum |
| 1 | Larger heads 15–25 mm diam.; outer phyllaries usually much shorter than inner phyllaries; glutinous ridge prominent, well developed, appearing dark brown on dry specimens | Cirsium cymosum var. canovirens |
"common" is not a number."fine" is not a number."fine" is not a number.