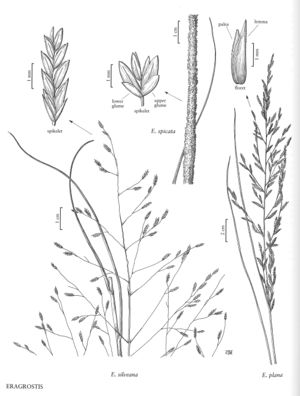
Eragrostis spicata
Plants perennial; cespitose, with innovations, without rhizomes. Culms 75-100 cm, erect, glabrous. Sheaths hirtellous on the margins when immature, apices glabrous or hairy shorter than 0.5 mm; ligules 0.2-0.3 mm; blades 20-40 cm long, 2-5 (6) mm wide, flat to involute, glabrous abaxially, scabrous adaxially. Panicles 22-40 cm long, 0.3-0.6 cm wide, spikelike, dense; primary branches shorter than 1.2 cm, closely appressed, spikelet-bearing to the base; pulvini glabrous; pedicels 0.1-0.6 mm, mostly appressed, hirtellous. Spikelets 1.4-2.2 mm long, 0.9-1.2 mm wide, ovate, stramineous to light greenish, with 2-3 florets; disarticulation basipetal, in the rachilla below the individual florets or at the base of the florets, glumes persistent. Glumes elliptic to ovate, hyaline, keels ciliolate; lower glumes 0.7-1 mm; upper glumes 0.9-1.3 mm, apices obtuse; lemmas 1.5-2.1 mm, ovate, membranous to hyaline, apices acute to obtuse; paleas 1.1-1.6 mm, hyaline, not wider than the lemmas, apices obtuse; anthers 2, 0.3-0.4 mm, reddish-brown. Caryopses 0.7-1 mm, ellipsoid, somewhat ventrally flattened, smooth to faintly striate, reddish-brown. 2n = 40.
Discussion
Eragrostis spicata grows in moist areas in prairies, usually in deep, sandy, clay loam soils, at 0-70 m. It is native from southern Texas to Mexico and in Paraguay and Argentina. In North America, it grows with Andropogon, Quercus stellata, Prosopsis glandulosa, and Acacia.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
"decumbent" is not a number.