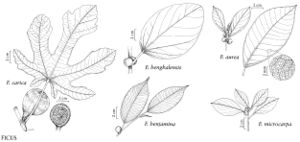
Ficus aurea
N. Amer. Sylv. 2: 4, plate 43. 1846.
Trees, evergreen, to 20 m. Roots aerial, sometimes present on branches, pendent, sometimes reaching ground and forming pillar-roots. Bark gray, smooth. Branchlets yellow. Leaves: stipules 1-1.5 cm; petiole 1-6 cm. Leaf-blade ovate to oblong or obovate, 6-12 (-15) × 3.5-6 cm, leathery, base rounded to cuneate, margins entire, apex obtuse or shortly and bluntly acuminate; surfaces abaxially and adaxially glabrous; basal veins 1 (-2) pairs; lateral-veins fewer than 10, if more these not uniformly spaced. Syconia usually paired, usually sessile, rarely with peduncles to 5 mm, red or yellow, obovoid, 6-15 mm diam., glabrous; subtending bracts 2, 3-5 mm, glabrous; ostiole prominent, closed by 3 conspicuous scales.
Phenology: Flowering spring–summer.
Habitat: Frequent in swamps, tropical hammocks, borders of mangrove swamps
Elevation: 0-10 m
Distribution
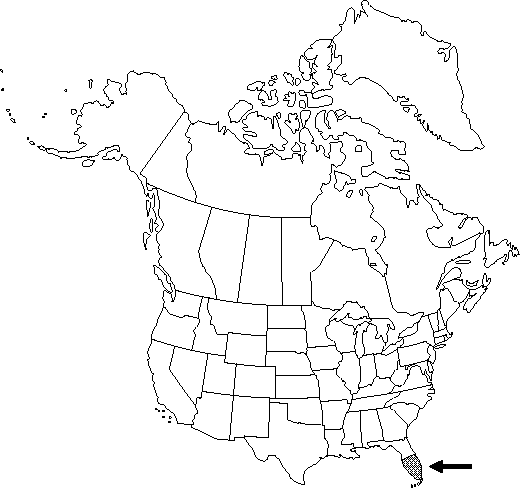
Fla., West Indies
Discussion
Selected References
None.