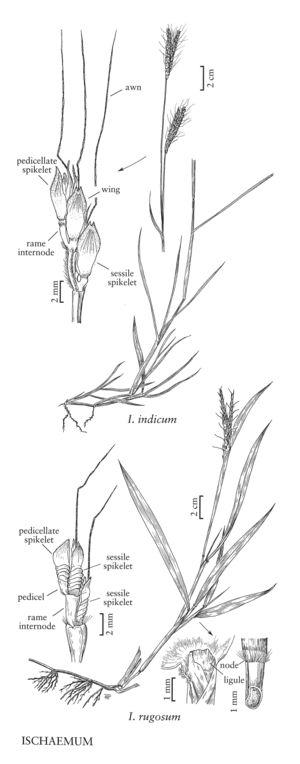
Ischaemum rugosum
Plants annual, or short-lived perennials. Culms 30-130 cm, erect or geniculate at the base, simple to strongly branched below; nodes antrorsely pilose; internodes glabrous. Leaves cauline; sheaths mostly glabrous or sparsely pilose, margins ciliate distally; collars villous; ligules 1-5.5 mm; blades 8-20 cm long, 7-15 mm wide, flat, usually pilose on both surfaces, sometimes with papillose-based hairs, occasionally glabrous. Inflorescence units with 2 rames; rames 3-8 cm long, 3-4 mm wide; internodes 2.5-3.5 mm, slightly clavate distally. Sessile spikelets 3-5 mm long, 1.8-2.2 mm wide; calluses shortly pubescent; lower glumes coriaceous, yellowish, not winged, coarsely transversely rugose with 4-5 ridges on the proximal 2/3 - 4/5, thickly chartaceous distally and tapering to the apices; upper glumes thickly chartaceous, ciliate, awned, awns 1.5-2 cm, geniculate below the middle; anthers about 2 mm. Pedicellate spikelets varying from 0.5 mm to equaling the sessile spikelets. 2n = 18, 20, 44.
Discussion
Ischaemum rugosum is native to southern Asia, and is now established in moist, tropical habitats around the world, including Mexico. It has been found in southern Texas and on chrome ore piles in Canton, Maryland, but is thought to have been eliminated from both areas. The U.S. Department of Agriculture considers it a noxious weed; plants found growing within the continental United States should be promptly reported to that agency.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
"decumbent" is not a number.