Leucolepis
Not. Sällsk. Fauna Fl. Fenn. Förh. 9: 80. 1868.
| Taxon | Illustrator ⠉ | |
|---|---|---|
 | Leucolepis acanthoneura | Patricia M. Eckel |
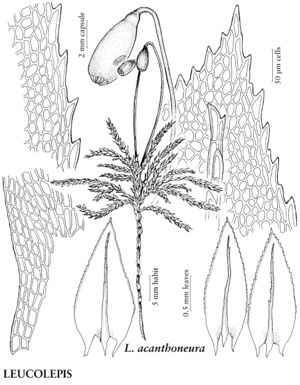
Plants 3–8 (–10) cm, in tufts or mats. Stems reddish-brown to black, erect, branched distally, dendroid; rhizoids brown, macronemata matted proximally, occasionally along stem into branched portion of stem, micronemata absent. Leaves dimorphic, pale to dark green or reddish-brown to hyaline, slightly contorted or crisped when dry, appressed or spreading, flat or keeled when moist, ovatelanceolate, (1.3–) 2–3 (–4) mm; base decurrent; margins plane, green, hyaline, or reddish-brown, 1-stratose, usually toothed to near base, teeth single, sharp; apex acute or long-acuminate, cuspidate or not; costa subpercurrent or percurrent, distal abaxial surface strongly toothed; medial laminal cells elongate, short-elongate, short-rhombic, or ± isodiametric, 17–50 µm, sometimes in longitudinal or diagonal rows, not or weakly collenchymatous, walls not pitted; marginal cells differentiated, linear, short-linear, or rhomboidal, in 1 or 2 rows. Specialized asexual reproduction absent. Sexual condition dioicous. Seta single or rarely double (or 3), reddish-brown, 4–5 cm, somewhat flexuose. Capsule pendent, yellowbrown or brown, cylindric, 6–8 mm; operculum hemispheric; exostome yellowbrown; endostome yellowbrown. Spores 28–30 µm.
Distribution
w North America
Discussion
Species 1.
Leucolepis is distinguished by a dendroid growth form and strongly differentiated stem leaves. Morphological (T. J. Koponen 1968) and cytological (R. J. Lowry 1948; W. C. Steere et al. 1954) research supports the split of Leucolepis from Mnium. The chromosome number of Leucolepis is n = 5, whereas Mnium is n = 6, 7, and 12.
Selected References
None.