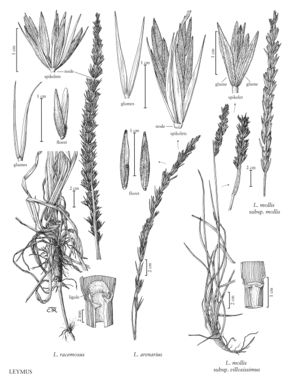
Leymus racemosus
Plants not or only weakly cespitose, strongly rhizomatous. often glaucous. Culms 50-100 cm tall, 8-12 mm thick, solitary or few together, mostly smooth and glabrous, scabridulous or pubescent below the spikes, hairs to 0.5 mm. Leaves exceeded by the spikes; ligules 1.5-2.5 mm; blades 20-40 cm long, 8-20 mm wide. Spikes 15-35 cm long, 10-20 mm wide, dense, with 3-8 spikelets per node; internodes 8-11 mm, surfaces hairy, hairs to 1 mm, on the edges to 1.5 mm. Spikelets 12-25 mm, sessile, with 4-6 florets. Glumes 12-25 mm long, to 2 mm wide, usually exceeding the lemmas, linear-lanceolate at the base, tapering from below midlength, stiff, glabrous at least at the base, the central portion thicker than the margins, keeled and subulate distally, 1-veined, veins inconspicuous at midlength; lemmas 15-20 mm, pubescent proximally, glabrous distally, tapering to an awn, awns 1.5-2.5 mm; palea keels usually glabrous, sometimes ciliate distally; anthers about 5 mm, dehiscent. 2n = 28.
Distribution
Wash., Minn., Mich., Ariz., Idaho, Nebr., Oreg., Wyo.
Discussion
Leymus racemosus is native to Europe and central Asia, where it grows on dry, sandy soils. It has been introduced into the Flora region, and collected at various locations, particularly in the northwestern contiguous United States; it is not clear how many of the populations represented by these specimens are still extant. Tsvelev (1976) recognized 4 subspecies. Because there are few North American specimens, and these are incomplete, no attempt has been made to determine to which subspecies the North American plants belong.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
"decumbent" is not a number."/2-33/4timesthelengthof" is not declared as a valid unit of measurement for this property.