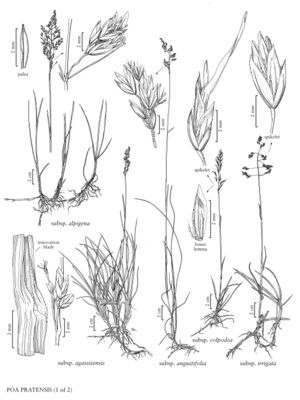
Poa pratensis subsp. colpodea
Plants strongly anthocyanic; moderately densely to loosely tufted, shoots solitary. Basal branching mainly extravaginal. Culms 15-30 cm. Innovation shoot blades shorter than 15 cm, 1-3.6 mm wide, flat or folded, soft, adaxial surfaces usually glabrous, sometimes sparsely pubescent; cauline blades flat or folded. Panicles 4-8 cm, narrowly pyramidal or contracted, with (1) 2-5 branches per node; branches 1-3 (5) cm, ascending or eventually spreading, smooth or sparsely scabrous, with several spikelets per branch. Spikelets narrowly lanceolate, bulbiferous, the least deformed spikelets 4-5.5 mm; florets mostly bulb-forming. Glume keels distinct, smooth or sparsely scabrous distally; upper glumes 2-2.5 (3) mm, nearly equaling the lowest lemmas; lemmas 2.5-3.5 mm, finely muriculate, lateral-veins glabrous; palea keels scabrous, frequently softly puberulent at midlength, intercostal regions usually glabrous, rarely sparsely hispidulous; anthers usually aborted, sometimes a few fairly well developed. 2n = ca. 27, 35, 35, 37, 38, 42, 51, 52, 56, 60, 66, 68, 69, 72, 73, 74, 75, 76, 77, 78, 79, 80, 81.
Discussion
Poa pratensis subsp. colpodea is circumpolar. In the Flora region, its range extends from Alaska and British Columbia to Greenland. It is more common than P. pratensis subsp. alpigena in the high arctic. The two sometimes grow together, and there is some evidence of a shift in dominance from year to year.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
"thin" is not a number."decumbent" is not a number.