Pogonatum
Mag. Encycl. 5: 329. 1804 ,.
| Taxon | Illustrator ⠉ | |
|---|---|---|
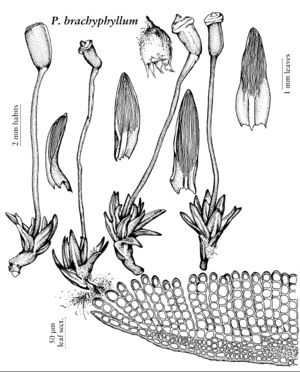 | Pogonatum brachyphyllum | Patricia M. Eckel |
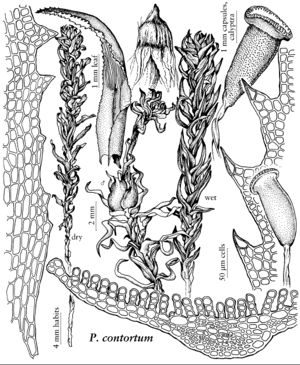 | Pogonatum contortum | Patricia M. Eckel |
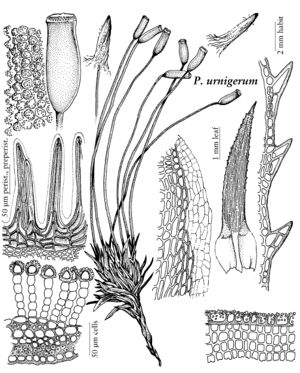 | Pogonatum urnigerum | Patricia M. Eckel |
Plants medium to large, in loose pure tufts or growing among other bryophytes, or individual stems small and scattered over a persistent protonemal mat. Stems simple or branched by subfloral innovations. Leaves with a sheathing base merging gradually or ± abruptly contracted to the blade, the sheath entire (toothed in P. contortum), with or without incrassate hinge-cells at the shoulders, not hyaline-margined (except in P. urnigerum); margins serrate, toothed, or entire, without a differentiated border of elongated cells; adaxial lamellae numerous and compact, occupying the full width of the blade, or somewhat fewer with an evident marginal lamina, marginal cells not differentiated, or strongly differentiated, thick-walled and coarsely papillose. Sexual condition dioicous; male plants similar to females in appearance, or budlike and inconspicuous. Seta smooth. Capsule ovoid to short-cylindric, ± regular to somewhat asymmetric, terete, sometimes with 4 or more indistinct angles or ridges; hypophysis not differentiated, tapering; stomata none; exothecium mammillose to scabrous, the exothecial cells mamillate or with a single papillate projection of the outer wall; operculum rostrate from a convex base; epiphragm persistent, attached to the peristome teeth; peristome deeply reddish pigmented (at least in the median line), the teeth 32, compound, with median sinus narrow or almost obliterated. Calyptra with a densely matted felt of hairs, covering most or all of the capsule. Spores finely papillose.
Distribution
North America, tropical America, Europe, Africa, Asia, Australasia, widespread in the tropics of both hemispheres, with only a few North temperate representatives
Discussion
Species 52 (5 in the flora).
North American species of Pogonatum vary greatly in size and habit from tall, laxly tufted plants to protonema mosses with individual plants scattered and only a few millimeters high. Pogonatum contortum of the Pacific Northwest, with leaves strongly crisped and contorted when dry, is the most “typical” of the genus as a whole. Pogonatum brachyphyllum and P. pensilvanicum are protonema-mosses, the gametophyte consisting of a persistent felted mat of protonema and leafy plants small and scattered. The other two species are distinctly polytrichoid in habit, with the margins of the lamellae thick-walled and coarsely papillose. Pogonatum dentatum is an arctic-montane species, whereas P. urnigerum has a somewhat more southerly distribution and occurs as well in the Himalayas and New Guinea. The sporophytes of our species are more uniform, with a scabrous exothecium, deeply pigmented peristome with compound peristome teeth, and no stomata. The exothecial “papillae” are projections of the cell wall, unlike the wart-like cuticular papillae often seen on the leaf surfaces of many Polytrichaceae.
Selected References
Lower Taxa
Key
| 1 | Plants to 0.6 cm, scattered over a green, persistent protonema | > 2 |
| 1 | Plants 3-8(-12) cm, in loose pure tufts or growing among other bryophytes | > 3 |
| 2 | Lamellae 25-40, compact, the leaf appearing thick and fleshy; leaf margins entire. | Pogonatum brachyphyllum |
| 2 | Lamellae 11-16, the leaf membranous; leaf margins irregularly notched. | Pogonatum pensilvanicum |
| 3 | Leaves toothed from the apex nearly to the base; marginal cells of lamellae not differentiated, smooth | Pogonatum contortum |
| 3 | Leaves toothed above the shoulders, the margins of the sheath entire; marginal cells of lamellae thick-walled and coarsely papillose | > 4 |
| 4 | Leaf margins with multicellular, hooked teeth; leaf sheath not hyaline-margined; marginal cells of lamellae ± rectangular, flat-topped, the lumen quadrate; peristome divided nearly to the base. | Pogonatum dentatum |
| 4 | Leaf margins with mostly 1-cellular teeth; leaf sheath hyaline-margined; marginal cells of lamellae rounded to transversely elliptical, the lumen pentagonal; peristome divided to ca. 0.6. | Pogonatum urnigerum |
"broadened" is not a number."elongated" is not a number.