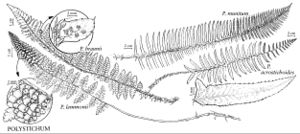
Polystichum lemmonii
Native Ferns ed. 6 116. 1900.
Stems decumbent to ascending. Leaves erect, 1–3.5 dm; bulblets absent. Petiole 1/5–1/4 length of leaf, sparsely scaly; scales pale tan, abruptly diminishing in size distally. Blade narrowly lanceolate, 2-pinnate, scarcely narrowed at base. Pinnae ovate, overlapping, folded inward and twisted horizontally, 0.5–2 cm; base truncate to oblique, proximal acroscopic pinnules not enlarged; apex broadly acute; microscales narrowly lanceolate, with few projections, sparse, ± confined to costa of both surfaces. Pinnules ± stalked, rounded, acroscopic auricle not well developed, margins entire to weakly dentate, apex rounded. Indusia entire or minutely dentate-erose. Spores dark-brown to blackish. 2n = 82.
Habitat: On rocky serpentine slopes
Elevation: 1200–2400 m
Distribution
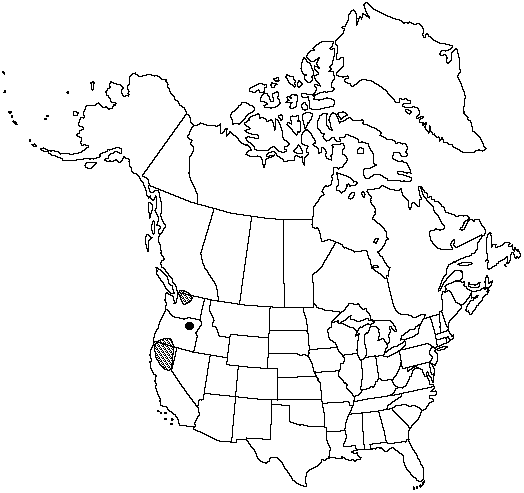
B.C., Calif., Oreg., Wash.
Discussion
Polystichum lemmonii forms sterile hybrids with P. scopulinum and P. munitum. The first hybrid may be abundant where the two parents grow together, which they frequently do in the Wenatchee Mountains of Washington and Siskiyou Mountains of northern California and southwest Oregon. The hybrid is very similar to P. lemmonii but has malformed sporangia and slightly less divided pinnae than P. lemmonii. The P. lemmonii × P. munitum hybrid is morphologically indistinguishable from P. scopulinum; it is a sterile diploid reported only twice from the Wenatchee Mountains of Washington (W. H. Wagner Jr. 1973; P. S. Soltis et al. 1989). It is possible that this hybrid involves P. imbricans and not P. munitum; neither study distinguished between them.
American authors have misapplied the name Polystichum mohrioides (Bory) C. Presl, a South American species, to P. lemmonii.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
"dm" is not declared as a valid unit of measurement for this property."/5lengthofleaf" is not declared as a valid unit of measurement for this property.