Pseudoleskea
in P. Bruch and W. P. Schimper, Bryol. Europ. 5: 147, plates 477, 478. 1852.
| Taxon | Illustrator ⠉ | |
|---|---|---|
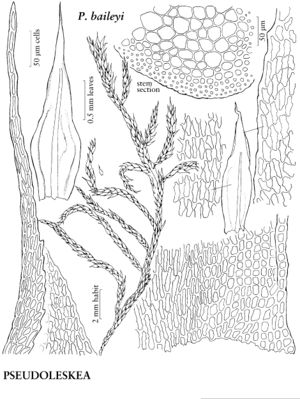 | Pseudoleskea baileyi | Patricia M. Eckel |
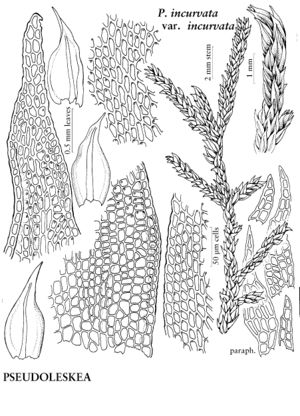 | Pseudoleskea incurvata | Patricia M. Eckel |
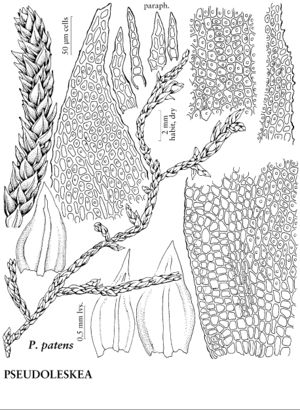 | Pseudoleskea patens | Patricia M. Eckel |
| ... further results | ||
Plants small to large, in thin to thick mats, green, yellow-green, orange-green, or gold-green, brown with age. Stems irregularly branched; paraphyllia many, few on older stems, or sometimes absent, filamentous to foliose, cells smooth or prorulose; rhizoids in clusters arising from base of stem-leaves. Stem and branch leaves similar. Stem-leaves appressed to julaceous when dry, erect-spreading when moist, ovate to lanceolate, weakly to strongly plicate on either side of costa; margins recurved proximally, entire to serrulate distally, limbidium present or absent; apex abruptly acute to long-acuminate, hairpoint present or absent; costa single, moderately strong, 2/3 leaf length to subpercurrent, opaque, not or weakly sinuate; alar cells transversely elongate, quadrate, or short-rectangular; proximal laminal cells similar to medial cells, usually shorter, 1–4: 1, walls pitted; medial cells quadrate to elongate-rhomboidal, 1–4: 1, 1-papillose to prorate, walls firm to thin; apical cells elongate. Specialized asexual reproduction absent. Sexual condition dioicous; perichaetial leaves pale translucent, erect when moist, longer, apex more acuminate, costa percurrent. Seta 0.8–1.2 cm. Capsule inclined, cylindric, asymmetric or symmetric; annulus absent; operculum smooth conic (conic-apiculate in P. baileyi); peristome well developed; exostome teeth lanceolate, striate to papillose; endostome basal membrane high, segments slender-lanceolate to filiform, cilia well developed to short and rudimentary. Spores 10–28 µm, papillose.
Distribution
North America, Eurasia, Atlantic Islands (Iceland)
Discussion
Species ca. 12 (8 in the flora).
Pseudoleskea are Northern Hemisphere species of montane to alpine regions found on rock and soil, typically in cool to cold climates. Pseudoleskea differs from Lescuraea in the shorter and mostly thicker-walled laminal cells and in the mostly perfect hypnoid peristome, showing some reduction in a few species. The stem leaves are weakly to strongly concave; the capsule is red to red-brown with bordered exostome teeth and 1–3 endostome cilia. J. R. Rohrer (1986) compared differences among the taxa. Pseudoleskea baileyi does not belong in the genus and appears to be closest morphologically to the eastern Asian Rigodiadelphus Dixon (M. U. Krieger 2002); it is included here for completeness.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
Key
| 1 | Medial laminal cells quadrate to elongate, papillose over lumen | > 2 |
| 1 | Medial laminal cells usually rhomboidal, prorate | > 4 |
| 2 | Leaf apices slenderly long-acuminate; medial laminal cells elongate-rhomboidal to fusiform or vermicular, most papillae off-centered on distal cell lumina; on bark and twigs of shrubs and trees. | Pseudoleskea stenophylla |
| 2 | Leaf apices short-acuminate to acute; medial laminal cells quadrate to isodiametric, papillae usually centered over lumina; on soil or rock, never corticolous | > 3 |
| 3 | Leaves appressed to julaceous when dry, usually larger than 0.8 mm; margins recurved proximally; laminal cells opaque, papillae low to large, not distinctly pointed-mammillose; costae with terminal projections short, not abaxially strongly dentate. | Pseudoleskea patens |
| 3 | Leaves catenulate, weakly incurved when dry, usually smaller than 0.8 mm; margins plane; laminal cells pellucid, papillae large, distinctly pointed-mammillose; costae with terminal projections strong, abaxially strongly dentate. | Pseudoleskea tribulosa |
| 4 | Leaf hair-points present; paraphyllia absent; costae ending in acumen but not percurrent; stems with central strand absent. | Pseudoleskea baileyi |
| 4 | Leaf hair-points absent; paraphyllia present; costae usually percurrent; stems with central strand present | > 5 |
| 5 | Stem leaf medial laminal cell walls distinctly and strongly pitted. | Pseudoleskea atricha |
| 5 | Stem leaf medial laminal cell walls not pitted | > 6 |
| 6 | Juxtacostal laminal cells somewhat longer than distal cells; medial laminal cells strongly prorate; margins broadly recurved to acumen; apices long- acuminate. | Pseudoleskea saviana |
| 6 | Juxtacostal laminal cells somewhat shorter than distal cells; medial laminal cells prorate; margins narrowly recurved to mid leaf or near acumen; apices acute to short- or rarely long-acuminate | > 7 |
| 7 | Apical cells 1-2:1; medial cell lumina smaller than 8 µm, walls incrassate, cell shape heterogeneous. | Pseudoleskea incurvata |
| 7 | Apical cells 2-3:1; medial cell lumina larger than 10 µm, walls thin, cell shape homogeneous. | Pseudoleskea radicosa |
"subpercurrent" is not a number."broad" is not a number.