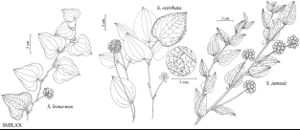
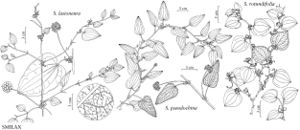
Shrubs, herbs, or vines, perennial, rhizomatous. Stems erect or climbing, usually prickly, sometimes unarmed. Leaves opposite or alternate, prominently 3-veined, reticulate between veins, usually bearing tendrils, usually leathery. Inflorescences umbellate [or racemose or spicate]. Flowers unisexual, staminate and pistillate on different plants; tepals 6, distinct, rarely united into perianth-tube; stamens 2–3-whorled, anthers 1-locular; pistillate flowers bearing staminodes, pistil 3-carpellate; ovary 2-locular, 1–2 ovules per locule. Fruits baccate. Seeds 1–3.
Distribution
Worldwide, mainly tropical to subtropical, a few temperate
Discussion
Genera 4(–12), species ca. 375 (1 genus, 20 species in the flora).
The leaves of Smilacaceae are atypical of monocotyledons in being reticulate between major veins. The family is closely related to and sometimes included in Liliaceae. It differs mainly in leaf characteristics and in being dioecious.
Selected References
None.