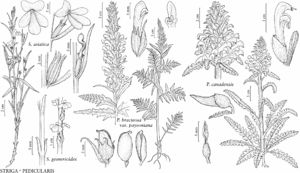
Striga gesnerioides
Oesterr. Bot. Z. 25: 11. 1875.
Annuals 15–30 cm; holoparasitic. Taproots stout, fleshy; secondary-roots absent; haustoria single, large, globular. Flowering-stems drying black or brown, simple or branched from base, obtusely square or terete, fleshy, puberulent, pilose, or glabrous. Leaves: blade opposite, appressed, lanceolate, scalelike, 3–7 x 2 mm, surfaces puberulent. Inflorescences spikes, lax, sometimes congested; flowers opposite, rarely alternate; bracts lanceolate, 5–7 x 1–2 mm, shorter than calyx, surfaces glabrous or puberulent. Flowers: sepals 5, 4–7 mm; calyx: tube 3–5 mm, ribs 5, scarious between ribs, teeth 5, unequal, subulate, 1–2 mm, adaxial shorter; corolla brownish red or purple, rarely white, sparsely pubescent or glabrous, tube bent, dilated distally above calyx, 8–12 mm, abaxial lobes 6 mm wide, adaxial 3–4 mm wide; style 5 mm, curved out, glabrous. Capsules oblong or ovoid, 4–5 x 2–3 mm. 2n = 40 (Nigeria).
Phenology: Flowering Aug–Oct.
Habitat: heavily disturbed phosphate mines, mine reclamation sites.
Elevation: 0–50 m.
Distribution
Introduced; Fla., Asia (Arabian Peninsula), Africa
Discussion
Worldwide, host-specific strains of Striga gesnerioides occur on Lepidagathis Willdenow (Acanthaceae), Ipomoea and Merremia (Convolvulaceae), Euphorbia (Euphorbiaceae), Indigofera, Tephrosia, and Vigna (Fabaceae), and Nicotiana (Solanaceae) (K. I. Mohamed et al. 2001); some of these may be potential hosts for this species in the flora area.
Striga gesnerioides was discovered in Florida in 1979 as a parasite on Indigofera hirsuta (hairy indigo), an African species planted for phosphate mine reclamation. Alysicarpus ovalifolius (alyce clover) is also attacked in the field but with much less frequency (L. Herbaugh et al. 1980; L. J. Musselman et al. 1980). Striga gesnerioides is known from Citrus, Hillsborough, Lake, Orange, Polk, Seminole, and Volusia counties (http://www.plantatlas.usf.edu/). Greenhouse experiments conducted in Florida on over 125 known potential hosts of S. gesnerioides (Herbaugh et al.) showed that it poses little threat to American agriculture (Musselman et al.). In addition to hairy indigo and alyce clover, the only other hosts reported in the Florida study were Jacquemontia tamnifolia, Helianthus annuus (sunflower), and Ipomoea batatas (sweet potato) (Herbaugh et al.). In an experiment conducted by Musselman and C. Parker (1981) on more than 30 potential hosts, the American strain of S. gesnerioides failed to grow on any of them except hairy indigo, showing the strict specificity of this strain.
Selected References
None.