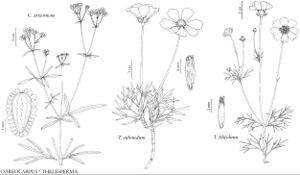
Thelesperma filifolium
Hooker’s J. Bot. Kew Gard. Misc. 1: 252. 1849.
Annuals (sometimes persisting), 10–40 (–70+) cm. Cauline leaves crowded to ± scattered over proximal 1/2–3/4 of plant heights, internodes mostly 10–35 (–50+) mm; lobes mostly linear to filiform, sometimes oblanceolate, 5–30 (–55+) × 0.5–1 (–3+) mm. Calyculi of 7–8+ linear to narrowly triangular bractlets (2–) 4–8+ mm. Ray-florets 8; laminae yellow to golden yellow (sometimes proximally suffused with redbrown), 12–20+ mm. Disc corollas redbrown or yellow with redbrown nerves, throats shorter than lobes. Cypselae 3.5–4+ mm; pappi 0.5–1 (–2+) mm. 2n = 16, 18.
Phenology: Flowering Mar–Aug(–Oct).
Habitat: Disturbed sites on clays or sandy soils, rocky slopes, often on limestone
Elevation: 10–2200 m
Distribution
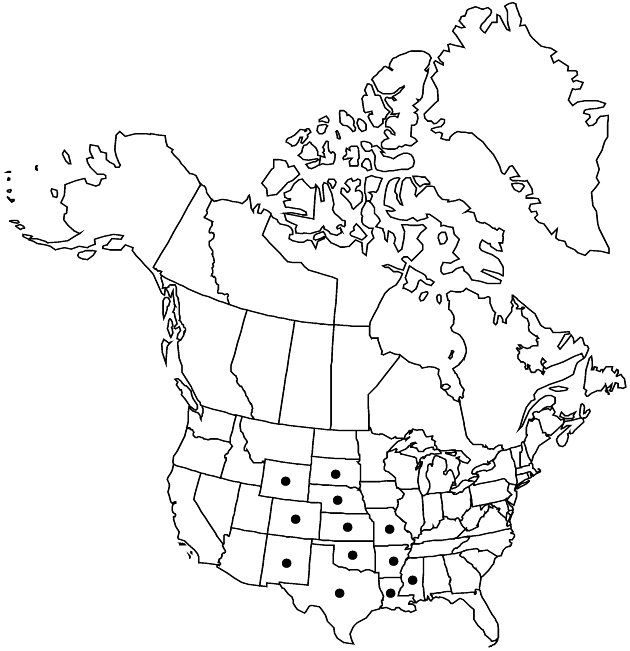
Ark., Colo., Kans., La., Miss., Mo., Nebr., N.Mex., Okla., S.Dak., Tex., Wyo., Mexico (Nuevo León)
Discussion
As here circumscribed, Thelesperma filifolium includes plants that others have treated as a distinct species or variety: T. intermedium or T. filifolium var. intermedium, characterized as plants mostly 10–40 cm (versus taller); internodes “relatively short” (versus longer); calyculus bractlets mostly 1/4–1/2 lengths of phyllaries (versus more than 1/2 as long); ray corollas yellow (versus “golden yellow”); disc corollas yellow (versus sometimes red-brown); distribution mostly north and west of the typical form (Colorado, Kansas, Nebraska, New Mexico, w Oklahoma, South Dakota, c and w Texas, Wyoming).
According to A. Cronquist (1980), Thelesperma trifidum (Poiret) Britton has been misapplied (e.g., M. L. Fernald 1950) to T. filifolium.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
"broader" is not a number.