Triplasis purpurea
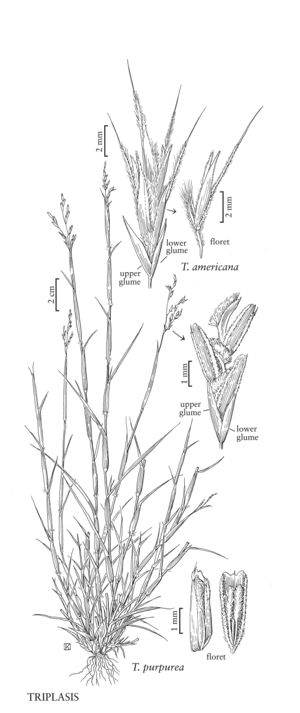
Plants annual and tufted or perennial and occasionally rhizomatous. Culms 14-100 cm, usually ascending; internodes glabrous. Ligules to 1 mm, of hairs; blades 1-5 mm wide, flat or involute, hispid or with papillose-based hairs. Panicles 3-7 cm long, 1-6 cm wide. Spikelets 6.5-9 mm, with 3-4 florets. Glumes about 2 mm, glabrous or scabrous, apices erose; lemmas 3-4 mm, lobes shorter than 1 mm, rounded; awns shorter than 2 mm, straight; paleas about 2.5 mm, keels ciliate; anthers about 2 mm, reddish-purple. Caryopses about 2 mm long, 0.6 mm wide, tapering distally, tan. 2n = 40.
Distribution
Conn., N.J., N.Y., Del., Wis., Fla., N.H., N.Mex., Tex., La., Tenn., N.C., S.C., Pa., Va., Colo., Ont., Ala., Kans., N.Dak., Nebr., Okla., S.Dak., Ark., Ill., Ga., Ind., Iowa, Ky., Maine, Md., Mass., Ohio, Mo., Mich., R.I., Miss., Oreg.
Discussion
Triplasis purpurea grows in sandy soils throughout the eastern and central portion of the Flora region, extending southward through Mexico to Costa Rica. It is far more common in maritime dunes than T. americana. Plants in the Flora region belong to Triplasis purpurea (Walter) Chapm. var. purpurea.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
"decumbent" is not a number.