Ammannia
Sp. Pl. 1: 119. 1753.
| Taxon | Illustrator ⠉ | |
|---|---|---|
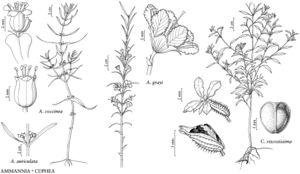 | Ammannia auriculata Ammannia grayi Cuphea viscosissima Ammania coccinea |
Herbs, annual or perennial, terrestrial or amphibious [aquatic], 1–10 dm, glabrous [puberulent]. Stems erect or trailing, glaucous or not throughout, branched or unbranched, anthocyanic in age, submerged stems sometimes thickened by aerenchymatous spongy tissue. Leaves opposite [subopposite or whorled]; sessile; blade linear, linear-lanceolate, oblong, linear-oblong, lanceolate, elliptic, or spatulate [ovate], base cordate or auriculate [attenuate]. Inflorescences indeterminate, axillary, simple or compound cymes or solitary flowers [racemes or capitula]. Flowers sessile, subsessile, or pedicellate, actinomorphic, monostylous [di or tristylous]; floral-tube perigynous, campanulate or urceolate, semiglobose to globose in fruit, often 8–12 [–16] -ribbed; epicalyx segments shorter than or as long as sepals [longer than or absent]; sepals 4–6 [–8], to 1/4 floral-tube length; petals caducous [persistent], (0–) 4–8, deep rose-purple, pale-pink, white, or pale lavender, sometimes with rose-purple midvein or basal spot, obovate to suborbiculate; nectariferous tissue present at ovary-floral tube junction; stamens 4–12 (–14) [–27]; ovary incompletely (1 or) 2–5-locular; placenta globose [elongate]; style slender and well-exserted or stout and included; stigma capitate or punctiform. Fruits capsules, walls thin and dry, indehiscent, splitting irregularly at maturity or initially circumscissile then splitting irregularly. Seeds [2–] 100+, obovoid to semiglobose, concave-convex, 0.3–0.4 × 0.3–0.5 mm; cotyledons ± complanate.
Distribution
North America, Mexico, West Indies, Central America, South America, Europe, Asia, Africa, Pacific Islands, Australia, worldwide in temperate to subtropical and tropical areas
Discussion
Species ca. 80 (5 in the flora).
Ammannia was expanded from ca. 25 species to ca. 80 with the inclusion of Hionanthera and Nesaea following multi-gene molecular phylogenetic evidence that the genera form a monophyly (S. A. Graham et al. 2011). Africa is the center of diversity for the genus.
Ammannia frequently grows with the closely similar Rotala ramosior. In the flora area, the auriculate leaf bases of Ammannia expediently separate it from Rotala; leaf bases are tapered in R. ramosior.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
Key
| 1 | Styles stout, 0.5 mm, included; petals 0–4(–6). | Ammannia latifolia |
| 1 | Styles slender, 1.5–9 mm, exserted; petals 4–6(–8). | > 2 |
| 2 | Inflorescences solitary flowers; peduncles 7–19 mm; petals 6, 4–7 mm; stigmas punctiform. | Ammannia grayi |
| 2 | Inflorescences simple or compound cymes (flowers sometimes solitary at proximalmost and distalmost nodes); peduncles 0–9 mm; petals 4(–8), 1.5–3 mm; stigmas capitate. | > 3 |
| 3 | Cymes 1–3(–5)-flowered mid stem; petals pale lavender, sometimes with rose purple midvein or rose purple basal spot; anthers light yellow. | Ammannia robusta |
| 3 | Cymes (1–)3–15-flowered mid stem; petals deep rose purple, sometimes with darker rose purple basal spot; anthers deep yellow. | > 4 |
| 4 | Peduncles slender (nearly filiform); cymes (3–)7–15-flowered mid stem; capsules (1–)1.5–2.5(–3.5) mm diam. | Ammannia auriculata |
| 4 | Peduncles stout; cymes (1–)3–7(–15)-flowered mid stem; capsules 3.5–5 mm diam. | Ammannia coccinea |