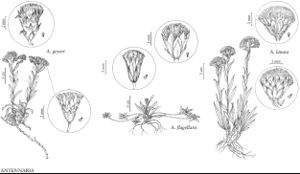
Antennaria flagellaris
Proc. Amer. Acad. Arts 17: 212. 1882.
Dioecious. Plants 0.5–1.5 cm. Stolons 3–10 cm (leafless except tips, relatively slender). Basal leaves 1-nerved, linear-oblanceolate, 16–18 × 1.5–2 mm, tips acute, faces ± gray-tomentose. Cauline leaves linear or oblanceolate, 7–15 mm, not flagged. Heads borne singly. Involucres: staminate 6–7 mm; pistillate 7–9 mm. Phyllaries (relatively wide) distally brown to blackish or whitish. Corollas: staminate 3–4.5 mm; pistillate 5–7 mm. Cypselae 2–3 mm, papillate; pappi: staminate 3.5–4.5 mm; pistillate 6–8 mm. 2n = 28.
Phenology: Flowering mid–late spring.
Habitat: Seasonally dry basins in foothills of mountains, often associated with sagebrush flats
Elevation: 900–2700 m
Distribution
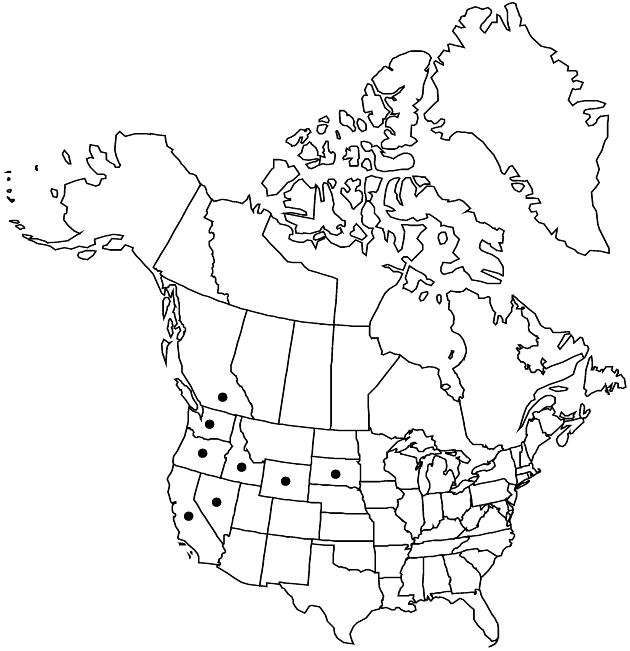
B.C., Calif., Idaho, Nev., Oreg., S.Dak., Wash., Wyo.
Discussion
Antennaria flagellaris is among the more distinctive species of Antennaria, with its flagelliform stolons (whiplike with leaves only at the very end) and heads borne singly. It belongs to the Dimorphae group (R. J. Bayer 1990; Bayer et al. 1996).
Selected References
None.