Arnica lanceolata
Trans. Amer. Philos. Soc., n. s. 7: 407. 1841.
Plants (5–) 20–80 cm. Stems solitary to densely clumped, simple or branched among heads. Leaves 4–8 (–10) pairs, mostly cauline; usually sessile (sometimes with partly connate-sheathing bases), sometimes petiolate (proximalmost); blades lance-elliptic, lanceolate, oblanceolate, obovate, or ovate, 4–12 (–20) × (1–) 2–6 (–8) cm, margins subentire to dentate-serrate, apices usually acute, rarely obtuse, faces glabrate to pilose. Heads (1–) 3–10 (–20). Involucres narrowly campanulate to turbinate. Phyllaries 8–15 (–19), narrowly to broadly lanceolate. Ray-florets (5–) 7–17 (–20); corollas yellow. Disc-florets: corollas yellow; anthers yellow. Cypselae brown, 4–8 mm, sparsely hirsutulous, stipitate-glandular; pappi tawny, bristles subplumose.
Distribution
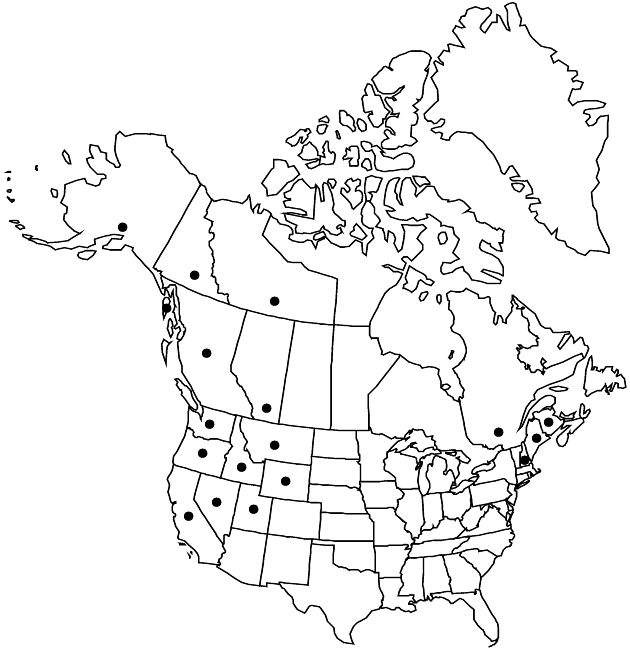
Alta., B.C., N.B., N.W.T., Que., Yukon, Alaska, Calif., Idaho, Maine, Mont., N.H., Nev., Oreg., Utah, Wash., Wyo.
Discussion
Subspecies 2 (2 in the flora).
Selected References
None.
Key
| 1 | Cauline leaves mostly sessile (proximalmost pair petiolate); e North America | Arnica lanceolata subsp. lanceolata |
| 1 | Cauline leaves sessile (including proximalmost pair, bases sometimes partly connate-sheathing); w North America | Arnica lanceolata subsp. prima |